A novel transcription factor-based signature to predict prognosis and therapeutic response of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36685838
- PMCID: PMC9845592
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1068837
A novel transcription factor-based signature to predict prognosis and therapeutic response of hepatocellular carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: A Novel transcription factor-based signature to predict prognosis and therapeutic response of hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 25;14:1146199. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1146199. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36798531 Free PMC article.
Abstract
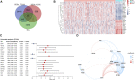
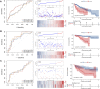
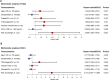
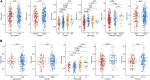
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common aggressive malignancies with increasing incidence worldwide. The oncogenic roles of transcription factors (TFs) were increasingly recognized in various cancers. This study aimed to develop a predicting signature based on TFs for the prognosis and treatment of HCC. Methods: Differentially expressed TFs were screened from data in the TCGA-LIHC and ICGC-LIRI-JP cohorts. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were applied to establish a TF-based prognostic signature. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to assess the predictive efficacy of the signature. Subsequently, correlations of the risk model with clinical features and treatment response in HCC were also analyzed. The TF target genes underwent Gene Ontology (GO) function and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses, followed by protein-protein-interaction (PPI) analysis. Results: A total of 25 differentially expressed TFs were screened, 16 of which were related to the prognosis of HCC in the TCGA-LIHC cohort. A 2-TF risk signature, comprising high mobility group AT-hook protein 1 (HMGA1) and MAF BZIP transcription factor G (MAFG), was constructed and validated to negatively related to the overall survival (OS) of HCC. The ROC curve showed good predictive efficiencies of the risk score regarding 1-year, 2-year and 3-year OS (mostly AUC >0.60). Additionally, the risk score independently predicted OS for HCC patients both in the training cohort of TCGA-LIHC dataset (HR = 2.498, p = 0.007) and in the testing cohort of ICGC-LIRI-JP dataset (HR = 5.411, p < 0.001). The risk score was also positively correlated to progressive characteristics regarding tumor grade, TNM stage and tumor invasion. Patients with a high-risk score were more resistant to transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) treatment and agents of lapatinib and erlotinib, but sensitive to chemotherapeutics. Further enrichment and PPI analyses demonstrated that the 2-TF signature distinguished tumors into 2 clusters with proliferative and metabolic features, with the hub genes belonging to the former cluster. Conclusion: Our study identified a 2-TF prognostic signature that indicated tumor heterogeneity with different clinical features and treatment preference, which help optimal therapeutic strategy and improved survival for HCC patients.
Keywords: MAF BZIP transcription factor G; hepatocellular carcinoma; high mobility group AT-hook protein 1; prognosis; therapeutic response; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Ye, Zhang, Lin, Fang, Wang, Yu, Hua, Huang, Xu, Liu and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel signature incorporating lipid metabolism- and immune-related genes to predict the prognosis and immune landscape in hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 6;13:1182434. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1182434. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37346073 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Ubiquitin-Specific Proteases as a Novel Prognostic Signature for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 25;11:629327. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.629327. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718205 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a Novel Four-Gene Signature Correlated With the Prognosis of Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 12;11:626654. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626654. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33777771 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Potential Hub Genes Related to Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Dec 8;2020:4251761. doi: 10.1155/2020/4251761. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33376723 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis-related molecular classification and gene signature of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental verification.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 31;13(3):1268-1289. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1876. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38617510 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcription factors-related molecular subtypes and risk prognostic model: exploring the immunogenicity landscape and potential drug targets in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jan 4;24(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03185-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38178084 Free PMC article.
-
The identification and prediction of lung adenocarcinoma prognosis using a novel gene signature associated with DNA replication.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 30;14(3):1971-1981. doi: 10.21037/tcr-2024-2536. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40224989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allemani C., Matsuda T., Di Carlo V., Harewood R., Matz M., Nikšić M., et al. (2018). Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 391 (10125), 1023–1075. 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)33326-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andreozzi M., Quintavalle C., Benz D., Quagliata L., Matter M., Calabrese D., et al. (2016). HMGA1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and promotes tumor growth and migration in in vitro models. Neoplasia 18 (12), 724–731. 10.1016/j.neo.2016.10.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bianconcini A., Lupo A., Capone S., Quadro L., Monti M., Zurlo D., et al. (2009). Transcriptional activity of the murine retinol-binding protein gene is regulated by a multiprotein complex containing HMGA1, p54 nrb/NonO, protein-associated splicing factor (PSF) and steroidogenic factor 1 (SF1)/liver receptor homologue 1 (LRH-1). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 41 (11), 2189–2203. 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.04.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

