Construction of HBV gene-related prognostic and diagnostic models for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36685852
- PMCID: PMC9845411
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1065644
Construction of HBV gene-related prognostic and diagnostic models for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
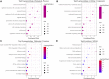
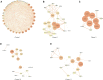
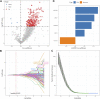
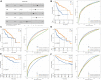
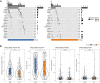
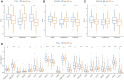
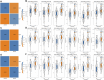
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a main cause of malignancy-related death all over the world with a poor prognosis. The current research is focused on developing novel prognostic and diagnostic models of Hepatocellular carcinoma from the perspective of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related genes, and predicting its prognostic characteristics and potential reliable biomarkers for Hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis. Methods: As per the information related to Hepatocellular carcinoma expression profile and the clinical data in multiple public databases, we utilized limma for assessing the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in HBV vs non- hepatitis B virus groups, and the gene set was enriched, analyzed and annotated by WebGestaltR package. Then, STRING was employed to investigate the protein interactions. A risk model for evaluating Hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis was built with Lasso Cox regression analysis. The effect patients receiving immunotherapy was predicted using Tumor Immune Dysfunction and Exclusion (TIDE). Additionally, pRRophetic was used to investigate the drug sensitivity. Lastly, the Support Vector Machine (SVM) approach was utilized for building the diagnostic model. Results: The Hepatocellular Carcinoma Molecular Atlas 18 (HCCDB18) data set was utilized for the identification of 1344 HBV-related differentially expressed genes, mainly associated with cell division activities. Five functional modules were established and then we built a prognostic model in accordance with the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network. Five HBV-related genes affecting prognosis were identified for constructing a prognostic model. Then, the samples were assigned into RS-high and -low groups as per their relevant prognostic risk score (RS). High-risk group showed worse prognosis, higher mutation rate of TP53, lower sensitivity to immunotherapy but higher response to chemotherapeutic drugs than low-risk group. Finally, the hepatitis B virus diagnostic model of Hepatocellular carcinoma was established. Conclusion: In conclusion, the prognostic and diagnostic models of hepatitis B virus gene-related Hepatocellular carcinoma were constructed. ABCB6, IPO7, TIMM9, FZD7, and ACAT1, the five HBV-related genes that affect the prognosis, can work as reliable biomarkers for the diagnosis of Hepatocellular carcinoma, giving a new insight for improving the prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment outcomes of HBV-type Hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: HBV; LIHC; immune microenvironment; molecular subtypes; prognostic characteristics.
Copyright © 2023 Ma, Wu and Ji.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer WN declared a shared parent affiliation with the authors KM and HW to the handling editor at the time of the review.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

