Enrichment of titin-truncating variants in exon 327 in dilated cardiomyopathy and its relevance to reduced nonsense-mediated mRNA decay efficiency
- PMID: 36685919
- PMCID: PMC9845391
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1087359
Enrichment of titin-truncating variants in exon 327 in dilated cardiomyopathy and its relevance to reduced nonsense-mediated mRNA decay efficiency
Abstract
Titin truncating variants (TTNtvs) are the most common genetic cause of dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). Among four regions of titin, A-band enrichment of DCM-causing TTNtvs is widely accepted but the underlying mechanism is still unknown. Meanwhile, few reports have identified exon 327 as a highly mutated A-band exon but the degree of exon 327 enrichment has not been quantitatively investigated. To find the real hotspot of DCM-causing TTNtvs, we aimed to reassess the degree of TTNtv enrichment in known titin regions and in exon 327, separately. In addition, we tried to explain exon 327 clustering in terms of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) efficiency and a dominant negative mechanism recently proposed. Research papers focusing on TTNtvs found in patients with DCM were collected. A total of 612 patients with TTNtv-realated DCM were obtained from 10 studies. In the four regions of TTN and exon 327, the degree of TTNtvs enrichment was calculated in a way that the effect of distribution of highly expressed exons was normalized. As a result, exon 327 was the only region that showed significant enrichment for DCM-related TTNtv (p < .001). On the other hand, other A-band exons had almost the same number of TTNtv of random distribution. A review of RNAseq data revealed that the median allelic imbalance deviation of exon 327 TTNtvs was .04, indicating almost zero NMD. From these findings, we propose that the widely accepted A-band enrichment of DCM-related TTNtv is mostly attributable to exon 327 enrichment. In addition, based on the recently demonstrated dominant negative mechanism, the extremely low NMD efficiency seems to contribute to exon 327 enrichment.
Keywords: TTN; dilated cardiomyopathy; exon 327; nonsense-mediated mRNA decay; truncating variant.
Copyright © 2023 Kim, Ha, Shin, Park, Jang and Kim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

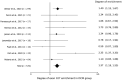
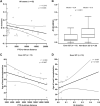

Similar articles
-
Reading Frame Repair of TTN Truncation Variants Restores Titin Quantity and Functions.Circulation. 2022 Jan 18;145(3):194-205. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.049997. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 34905694 Free PMC article.
-
Truncated titin proteins in dilated cardiomyopathy.Sci Transl Med. 2021 Nov 3;13(618):eabd7287. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd7287. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Sci Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34731015 Free PMC article.
-
TTN:c.12478del in proximal I-band of titin represents a common molecular cause of dilated cardiomyopathy in Slovenian patients.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Feb 28;20(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03613-7. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40022161 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic epidemiology of titin-truncating variants in the etiology of dilated cardiomyopathy.Biophys Rev. 2017 Jun;9(3):207-223. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0265-7. Epub 2017 May 5. Biophys Rev. 2017. PMID: 28510119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Titin mutations and muscle disease.Pflugers Arch. 2019 May;471(5):673-682. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02272-5. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30919088 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of TTN Truncating Variants in >74 000 Cases Reveals New Clinically Relevant Gene Regions.Circ Genom Precis Med. 2025 Apr;18(2):e004982. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.124.004982. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2025. PMID: 39968638 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of NEB pathogenic variants in patients reveals novel nemaline myopathy disease mechanisms and omecamtiv mecarbil force effects.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Apr 18;147(1):72. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02726-w. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 38634969 Free PMC article.
-
Pathomechanisms of Monoallelic variants in TTN causing skeletal muscle disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2024 Nov 20;33(23):2003-2023. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddae136. Hum Mol Genet. 2024. PMID: 39277846 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

