A machine learning-based approach to ERα bioactivity and drug ADMET prediction
- PMID: 36685926
- PMCID: PMC9845410
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1087273
A machine learning-based approach to ERα bioactivity and drug ADMET prediction
Abstract
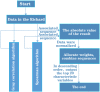
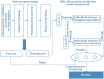
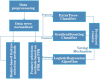
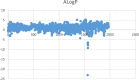
By predicting ERα bioactivity and mining the potential relationship between Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity (ADMET) attributes in drug research and development, the development efficiency of specific drugs for breast cancer will be effectively improved and the misjudgment rate of R&D personnel will be reduced. The quantitative prediction model of ERα bioactivity and classification prediction model of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity properties were constructed. The prediction results of ERα bioactivity were compared by XGBoot, Light GBM, Random Forest and MLP neural network. Two models with high prediction accuracy were selected and fused to obtain ERα bioactivity prediction model from Mean absolute error (MAE), mean squared error (MSE) and R2. The data were further subjected to model-based feature selection and FDR/FPR-based feature selection, respectively, and the results were placed in a voting machine to obtain Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity classification prediction model. In this study, 430 molecular descriptors were removed, and finally 20 molecular descriptors with the most significant effect on biological activity obtained by the dual feature screening combined optimization method were used to establish a compound molecular descriptor prediction model for ERα biological activity, and further classification and prediction of the Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity properties of the drugs were made. Eighty variables were selected by the model ExtraTreesClassifier Classifie, and 40 variables were selected by the model GradientBoostingClassifier to complete the model-based feature selection. At the same time, the feature selection method based on FDR/FPR is also selected, and the three classification models obtained by the two methods are placed into the voting machine to obtain the final model. The experimental results showed that the model's evaluation indexes and roc diagram were excellent and could accurately predict ERα bioactivity and Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity properties. The model constructed in this study has high accuracy, fast convergence and robustness, has a very high accuracy for Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity and ERα classification prediction, has bright prospects in the biopharmaceutical field, and is an important method for energy conservation and yield increase in the future.
Keywords: ADMET; ERα bioactivity; breast cancer; drug development; machine learning.
Copyright © 2023 An, Chen, Chen, Ma, Wang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prediction and Screening Model for Products Based on Fusion Regression and XGBoost Classification.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 31;2022:4987639. doi: 10.1155/2022/4987639. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35958779 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the optimization model of anti-breast cancer candidate drugs based on machine learning.Front Genet. 2025 Apr 10;16:1523015. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1523015. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40276676 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization Modeling of Anti - breast Cancer Candidate Drugs.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024 Oct;40(2):1334-1352. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2193484. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2024. PMID: 36960749 Review.
-
MLP-Based Regression Prediction Model For Compound Bioactivity.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jul 13;10:946329. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.946329. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35910022 Free PMC article.
-
Promises of Machine Learning Approaches in Prediction of Absorption of Compounds.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(3):196-207. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170315150116. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28302041 Review.
Cited by
-
Adapting physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models for machine learning applications.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 11;13(1):14934. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42165-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37696914 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging machine learning models in evaluating ADMET properties for drug discovery and development.ADMET DMPK. 2025 Jun 7;13(3):2772. doi: 10.5599/admet.2772. eCollection 2025. ADMET DMPK. 2025. PMID: 40585410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hybrid deep learning technique for COX-2 inhibition bioactivity detection against breast cancer disease.Biomed Eng Lett. 2024 Apr 10;14(4):631-647. doi: 10.1007/s13534-024-00355-6. eCollection 2024 Jul. Biomed Eng Lett. 2024. PMID: 39512384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Casteleiro-Roca J. L., Jove E., Gonzalez-Cava J. M., Mendez Perez J. A., Calvo-Rolle J. L., Blanco Alvarez F. (2020). Hybrid model for the ANI index prediction using Remifentanil drug and EMG signal. Neural comput. Appl. 32, 1249–1258. 10.1007/s00521-018-3605-z - DOI
-
- Chang Y. H., Chen J. Y., Hor C. Y., Chuang Y. C., Yang C. B., Yang C. N. (2013). Computational study of estrogen receptor-alpha antagonist with three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship, support vector regression, and linear regression methods. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 743139. 10.1155/2013/743139 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dejun Y., Xiangcao Y., Chongyuan X., Shilin Z., Huang (2018). Molecular docking of uric acid-lowering activity and ADMET properties of small molecule compounds from red fennel. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 34 (23), 2750–2752+2777. 10.13699/j.cnki.1001-6821.2018.23.019 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

