Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis and the regulatory mechanism of AURKA, a gene associated with prognosis of ferroptosis of adrenal cortical carcinoma in the tumor micro-environment
- PMID: 36685952
- PMCID: PMC9845395
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.996180
Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis and the regulatory mechanism of AURKA, a gene associated with prognosis of ferroptosis of adrenal cortical carcinoma in the tumor micro-environment
Abstract
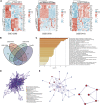
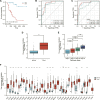
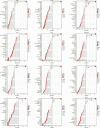
Background: The only curative option for patients with locally or locally advanced adrenocortical carcinoma is primary tumor curative sexual resection (ACC). However, overall survival remains low, with most deaths occurring within the first 2 years following surgery. The 5-year survival rate after surgery is less than 30%. As a result, more accurate prognosis-related predictive biomarkers must be investigated urgently to detect patients' disease status after surgery. Methods: Data from FerrDb were obtained to identify ferroptosis-related genes, and ACC gene expression profiles were collected from the GEO database to find differentially expressed ACC ferroptosis-related genes using differential expression analysis. The DEFGs were subjected to Gene Ontology gene enrichment analysis and KEGG signaling pathway enrichment analysis. PPI network building and predictive analysis were used to filter core genes. The expression of critical genes in ACC pathological stage and pan-cancer was then investigated. In recent years, immune-related factors, DNA repair genes, and methyltransferase genes have been employed in diagnosing and prognosis of different malignancies. Cancer cells are mutated due to DNA repair genes, and highly expressed DNA repair genes promote cancer. Dysregulation of methyltransferase genes and Immune-related factors, which are shown to be significantly expressed in numerous malignancies, also plays a crucial role in cancer. As a result, we investigated the relationship of AURKA with immunological checkpoints, DNA repair genes, and methyltransferases in pan-cancer. Result: The DEGs found in the GEO database were crossed with ferroptosis-related genes, yielding 42 differentially expressed ferroptosis-related genes. Six of these 42 genes, particularly AURKA, are linked to the prognosis of ACC. AURKA expression was significantly correlated with poor prognosis in patients with multiple cancers, and there was a significant positive correlation with Th2 cells. Furthermore, AURKA expression was positively associated with tumor immune infiltration in Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), Liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), Sarcoma (SARC), Esophageal carcinoma (ESCA), and Stomach adenocarcinoma (STAD), but negatively correlated with the immune score, matrix score, and calculated score in these tumors. Further investigation into the relationship between AURKA expression and immune examination gene expression revealed that AURKA could control the tumor-resistant pattern in most tumors by regulating the expression level of specific immune examination genes. Conclusion: AURKA may be an independent prognostic marker for predicting ACC patient prognosis. AURKA may play an essential role in the tumor microenvironment and tumor immunity, according to a pan-cancer analysis, and it has the potential to be a predictive biomarker for multiple cancers.
Keywords: AURKA; ferroptosis; pan-cancer analysis; regulatory mechanism; tumor micro-environment.
Copyright © 2023 Lu, Yuan, Zhao, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identifies microtubule-binding protein CSPP1 as a novel cancer biomarker associated with ferroptosis and tumor microenvironment.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 24;20:3322-3335. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.046. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35832625 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SHCBP1 as a potential biomarker involving diagnosis, prognosis, and tumor immune microenvironment across multiple cancers.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 18;20:3106-3119. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.039. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35782736 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Pan-Cancer Analysis and the Regulatory Mechanism of ASF1B, a Gene Associated With Thyroid Cancer Prognosis in the Tumor Micro-Environment.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 20;11:711756. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.711756. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34490109 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis-related NFE2L2 and NOX4 Genes are Potential Risk Prognostic Biomarkers and Correlated with Immunogenic Features in Glioma.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023 Mar;81(1):7-17. doi: 10.1007/s12013-022-01124-x. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2023. PMID: 36627482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 3 (CDKN3) in promoting human tumors: Literature review and pan-cancer analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 8;10(4):e26061. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26061. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38380029 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of key genes and pathways in adrenocortical carcinoma: evidence from bioinformatic analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 20;14:1250033. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1250033. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38053725 Free PMC article.
-
Role of non-coding RNA-regulated ferroptosis in colorectal cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Jul 8;11(1):315. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02606-6. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40628711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional control drives Aurora kinase A expression in human cancers.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 11;19(11):e0310625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310625. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39527514 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of susceptibility modules and hub genes of adrenocortical carcinoma through WGCNA and machine learning.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 3;16(1):663. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02396-4. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40317315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Q., Wang W., Wu Z., Chen S., Chen X., Zhuang S., et al. (2021). Over-expression of lncRNA TMEM161B-AS1 promotes the malignant biological behavior of glioma cells and the resistance to temozolomide via up-regulating the expression of multiple ferroptosis-related genes by sponging hsa-miR-27a-3p. Cell Death Discov. 7, 311. 10.1038/s41420-021-00709-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

