Coding roles of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: Emerging molecular diagnostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets with special reference to chemotherapy resistance
- PMID: 36685962
- PMCID: PMC9852779
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.993687
Coding roles of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: Emerging molecular diagnostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets with special reference to chemotherapy resistance
Abstract
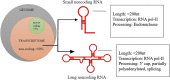
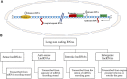
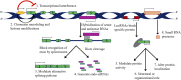
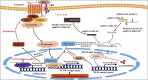
Dysregulation of epigenetic mechanisms have been depicted in several pathological consequence such as cancer. Different modes of epigenetic regulation (DNA methylation (hypomethylation or hypermethylation of promotor), histone modifications, abnormal expression of microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs, and small nucleolar RNAs), are discovered. Particularly, lncRNAs are known to exert pivot roles in different types of cancer including breast cancer. LncRNAs with oncogenic and tumour suppressive potential are reported. Differentially expressed lncRNAs contribute a remarkable role in the development of primary and acquired resistance for radiotherapy, endocrine therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. A wide range of molecular subtype specific lncRNAs have been assessed in breast cancer research. A number of studies have also shown that lncRNAs may be clinically used as non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for early detection of breast cancer. Such molecular biomarkers have also been found in cancer stem cells of breast tumours. The objectives of the present review are to summarize the important roles of oncogenic and tumour suppressive lncRNAs for the early diagnosis of breast cancer, metastatic potential, and chemotherapy resistance across the molecular subtypes.
Keywords: breast cancer; chemotherapeutic resistance; early diagnosis; long non-coding RNAs; non-invasive biomarkers; oncogenic lncRNA; tumour supressive lncRNA.
Copyright © 2023 Kashyap, Sharma, Goel, Buttar, Garg, Pal, Rajab and Shaikh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNAs: implications in targeted diagnoses, prognosis, and improved therapeutic strategies in human non- and triple-negative breast cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2018 Jun 27;10:88. doi: 10.1186/s13148-018-0514-z. eCollection 2018. Clin Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29983835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) signaling in cancer chemoresistance: From prediction to druggability.Drug Resist Updat. 2022 Dec;65:100866. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2022.100866. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Drug Resist Updat. 2022. PMID: 36198236 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs as monitoring tools and therapeutic targets in breast cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019 Feb;42(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s13402-018-0412-6. Epub 2018 Oct 25. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019. PMID: 30361825 Review.
-
Combinatorial epigenetic regulation of non-coding RNAs has profound effects on oncogenic pathways in breast cancer subtypes.Brief Bioinform. 2018 Jan 1;19(1):52-64. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw099. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 27742663
-
Roles of Oncogenic Long Non-coding RNAs in Cancer Development.Genomics Inform. 2018 Dec;16(4):e18. doi: 10.5808/GI.2018.16.4.e18. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Genomics Inform. 2018. PMID: 30602079 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Omics-Based Investigations of Breast Cancer.Molecules. 2023 Jun 14;28(12):4768. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124768. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Delivery of Potent Chemical Drugs and RNAi to Drug-Resistant Breast Cancer Using RNA-Nanotechnology and RNA-Ligand Displaying Extracellular vesicles.RNA Nanomed. 2024;1(1):16-43. doi: 10.59566/isrnn.2024.0101016. RNA Nanomed. 2024. PMID: 40125243 Free PMC article.
-
Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs and BRCA1 in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis: Neighboring Companions or Nemeses?Noncoding RNA. 2025 Jan 29;11(1):9. doi: 10.3390/ncrna11010009. Noncoding RNA. 2025. PMID: 39997609 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelaleem O. O., Shaker O. G., Abdelhafez M. N., Abdelghaffar N. K., Eid H. M., Zaidan M., et al. (2021). The influence of rs1859168 polymorphism on serum expression of hottip and its target mir‐615‐3p in egyptian patients with breast cancer. Biomolecules 11, 733. 10.3390/biom11050733 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali M. A., Shaker O. G., Alazrak M., Abdelhafez M. N., Khalefa A. A., Hemeda N. F., et al. (2020). Association analyses of a genetic variant in long non-coding RNA MEG3 with breast cancer susceptibility and serum MEG3 expression level in the Egyptian population. Cancer Biomark. 28, 49–63. 10.3233/CBM-191072 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

