A Case of Empyema Due to Actinomyces odontolyticus and Streptococcus Species Co-infection in an Immunocompetent Woman
- PMID: 36686073
- PMCID: PMC9853470
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32700
A Case of Empyema Due to Actinomyces odontolyticus and Streptococcus Species Co-infection in an Immunocompetent Woman
Abstract
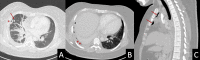
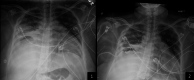
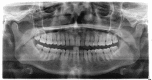
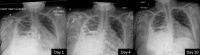
Actinomyces species are opportunistic pathogens, difficult to isolate, and often accompanied by other pathogens. We report the case of an immunocompetent woman who presented with respiratory distress and was discovered to have a right-sided empyema requiring chest tube drainage. Streptococcus species and Actinomyces odontolyticus were isolated in pleural fluid cultures. Initial empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy and chest tube placement failed to show clinical improvement. Upon isolation of Actinomyces, the treatment was streamlined to ampicillin/sulbactam while pleural drainage continued, producing significant clinical status improvement in the patient. Given the known co-pathogenicity of Actinomyces species and the difficulty in isolating Actinomyces, it is essential to consider antibiotic coverage for Actinomyces species in those with Streptococcus species empyema.
Keywords: actinomyces odontolyticus; co-infection; empyema; immunocompetent; streptococcus species.
Copyright © 2022, Peralta et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Empyema caused by Actinomyces odontolyticus: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Feb 2;103(5):e37003. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037003. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38306531 Free PMC article.
-
[A case of empyema due to Capnocytophaga sp. and Actinomyces israelii].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2009 Oct;47(10):906-11. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19882914 Japanese.
-
A Case of Thoracic Empyema Caused by Actinomyces naeslundii.Am J Case Rep. 2024 Feb 18;25:e943030. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.943030. Am J Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38368503 Free PMC article.
-
A case report of esophageal actinomycosis in an immunocompetent patient and review of the literature.New Microbiol. 2019 Jan;42(1):55-60. Epub 2019 Feb 20. New Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30785207 Review.
-
Empyema caused by Streptococcus constellatus: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Dec 20;21(1):1267. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06955-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34930151 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lemierre Syndrome involving Schaalia (Formerly Actinomyces) odontolyticus due to injection drug use into the neck.IDCases. 2024 Oct 20;38:e02104. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2024.e02104. eCollection 2024. IDCases. 2024. PMID: 39553249 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2019. Agents of actinomycosis; pp. 3071–3081.
-
- Human actinomycosis. A study of 181 subjects. Brown JR. Hum Pathol. 1973;4:319–330. - PubMed
-
- A study of 57 cases of actinomycosis over a 36-year period. A diagnostic 'failure' with good prognosis after treatment. Weese WC, Smith IM. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1200725. Arch Intern Med. 1975;135:1562–1568. - PubMed
-
- Resistance patterns in clinical isolates of pathogenic Actinomyces species. Steininger C, Willinger B. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71:422–427. - PubMed
-
- Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Actinomyces species with 12 antimicrobial agents. Smith AJ, Hall V, Thakker B, Gemmell CG. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;56:407–409. - PubMed
