The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on the Relation Between Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4) and Vitamin D Plasma Levels in Male Obese Population
- PMID: 36686076
- PMCID: PMC9851569
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32733
The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on the Relation Between Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4) and Vitamin D Plasma Levels in Male Obese Population
Abstract
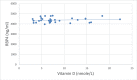
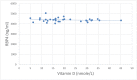
Objectives Obesity is viewed as a risk factor for several life-threatening diseases. Bariatric surgeries are regarded as a safe and effective way of treating morbid obesity and are associated with alterations in molecules such as Vitamin D and retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4). The aim of this study was to examine an association between Vitamin D and RBP4 in healthy obese individuals undergoing gastric sleeve surgery. Methods In this observational retrospective cohort study, we used clinical and biochemical profiles of morbidly obese healthy male subjects (BMI > 38.3) who underwent laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. RBP4 levels were evaluated by ELISA before and 6-12 months after surgery. Data were analysed using SPSS 23 statistical software. Results RBP4/Vitamin D ratio was reduced significantly after surgery (p < 0.001), however, there was no correlation between Vitamin D and RBP4 (p = 0.353). BMI was reduced significantly after surgery (p < 0.001) but was not correlated with RBP4 or Vitamin D levels before and after surgery (p > 0.05). A significant increase in the levels of calcium post-surgery was observed (p< 0.001). Conclusions In conclusion, plasma levels of Vitamin D were not correlated with RBP4 before or after laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery.
Keywords: bariatric surgery; obesity; retinol-binding protein 4 (rbp4); saudi arabia; vitamin d.
Copyright © 2022, Faqihi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Gastric Sleeve Surgery on Plasma Retinol Binding Protein 4 and Adipsin Levels in Healthy Male Population.Pak J Med Sci. 2020 Nov-Dec;36(7):1495-1499. doi: 10.12669/pjms.36.7.2329. Pak J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33235563 Free PMC article.
-
Changes of serum retinol-binding protein 4 associated with improved insulin resistance after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in Chinese obese patients.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020 Jan 14;12:7. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0511-1. eCollection 2020. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 31956345 Free PMC article.
-
High Incidence of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Bariatric Patients: Comparing Different Procedures.Obes Surg. 2018 Mar;28(3):798-804. doi: 10.1007/s11695-017-2932-y. Obes Surg. 2018. PMID: 28921422
-
Long-term impact of vertical banded gastroplasty (VBG) on plasma concentration of leptin, soluble leptin receptor, ghrelin, omentin-1, obestatin, and retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) in patients with severe obesity.Cytokine. 2013 Nov;64(2):490-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.07.026. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Cytokine. 2013. PMID: 24011638
-
Vitamin A in regulation of insulin responsiveness: mini review.Proc Nutr Soc. 2016 May;75(2):212-5. doi: 10.1017/S0029665115004322. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Proc Nutr Soc. 2016. PMID: 26729422 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Retinol-Binding Protein 4 (RBP4): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Obes Surg. 2024 May;34(5):1855-1865. doi: 10.1007/s11695-024-07140-5. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Obes Surg. 2024. PMID: 38451368
-
State of art on the mechanisms of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus.World J Diabetes. 2023 Jun 15;14(6):632-655. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i6.632. World J Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37383590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- A review of prevalence of obesity in Saudi Arabia. M Alqarni SS. J Obes Eat Disord. 2016;2:2.
-
- Nutritional deficiencies following bariatric surgery: what have we learned? Bloomberg RD, Fleishman A, Nalle JE, Herron DM, Kini S. Obes Surg. 2005;15:145–154. - PubMed
-
- Bariatric surgery in Saudi Arabia: the urgent need for standards. Al-Khaldi YM. Saudi J Obesity. 2016;4:1.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous