The Impact of Pulmonary Rehabilitation in a Case of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome With Bronchopneumonia: A Case Report
- PMID: 36686089
- PMCID: PMC9848687
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32671
The Impact of Pulmonary Rehabilitation in a Case of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome With Bronchopneumonia: A Case Report
Abstract
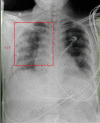
Inhaled bacteria and viruses could cause pneumonia (from the Greek word pneuma, which means "breath"), which is an infection and inflammation of the bronchioles and alveoli in the lower respiratory tract that can be fatal. The condition's typical symptoms include excruciating chest pain and a persistent cough that produces thick mucus. Of patients in emergency medicine units around the world, 10% have acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). A 35-year-old male patient stated having a fever for 12 days, a cough with expectoration for two days, and trouble breathing at rest when he arrived at the medical emergency unit. Following the examination, blood investigation, urine examination, and X-ray were done suggestive of bronchopneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome. The patient was assessed using a range of outcome measures on the assessment day, and the same variables were again assessed on the discharge and follow-up days. These outcome measures showed significant reduction in the severity of the cough and dyspnea. Also, the patient had markedly improved cough intensity, dyspnea (Modified Medical Research Council {MMRC}, grade 2), lung capacity, weakness, and quality of life (QoL) because of our well-organized pulmonary rehabilitation. It is safe to assume that a thorough strategy like ours will lead to an improvement in the patient's respiratory health.
Keywords: ards; physical therapy; physiotherapy; pneumonia; pulmonary rehabilitation.
Copyright © 2022, Nandanwar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physiotherapy Approach for Treating Bronchopneumonia: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Dec 28;15(12):e51246. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51246. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38288235 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chest Physiotherapy on Reducing Dyspnea and Enhancing Functional Independence and Quality of Life in Multilobar Pneumonia: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Oct 4;16(10):e70868. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70868. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39497873 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical analysis of the first patient with imported Middle East respiratory syndrome in China].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Aug;27(8):630-4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2015.08.002. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26255008 Chinese.
-
Pulmonary Manifestations of Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) Syndrome: A Systematic Review.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Sep 24;2019:7863815. doi: 10.1155/2019/7863815. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31662996 Free PMC article.
-
Lung function and quality of life in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).Presse Med. 2011 Dec;40(12 Pt 2):e595-603. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2011.04.024. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Presse Med. 2011. PMID: 22078086 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiotherapy Approach for Treating Bronchopneumonia: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Dec 28;15(12):e51246. doi: 10.7759/cureus.51246. eCollection 2023 Dec. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38288235 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chest Physiotherapy on Reducing Dyspnea and Enhancing Functional Independence and Quality of Life in Multilobar Pneumonia: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Oct 4;16(10):e70868. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70868. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39497873 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of alveolar lavage fluid improves the detection of pulmonary infection.Open Life Sci. 2025 May 12;20(1):20251074. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1074. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40391192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. [ Sep; 2022 ];Luce JM. Crit Care Med. 1998 26:369–376. - PubMed
-
- Leukocytes are required for increased lung microvascular permeability after microembolization in sheep. [ Sep; 2023 ];Flick MR, Perel A, Staub NC. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/01.res.48.3.344. Circ Res. 1981 48:344–351. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources