Joys or Sorrows of Parenting During the COVID-19 Lockdown: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 36686329
- PMCID: PMC9845277
- DOI: 10.3389/phrs.2022.1605263
Joys or Sorrows of Parenting During the COVID-19 Lockdown: A Scoping Review
Abstract
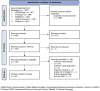
Objectives: The aim of this scoping review was to map out the existing evidence of the impact of the COVID-19 lockdown on parents of children and adolescents. We sought to: 1) identify parenting domains that were particularly affected by lockdown measures, 2) describe the challenges and opportunities of lockdown measures in these domains, and 3) define protective and exacerbating factors modulating the effect of lockdown measures on parents. Methods: We identified five main domains investigated in the context of parenting during the early COVID-19 lockdown derived from 84 studies: health and wellbeing, parental role, couple functioning, family and social relationships, and paid and unpaid work. For each domain, we listed challenges and opportunities, as well as discriminant factors. Results: The lockdown impacted all five different but interconnected domains, introduced new roles in parents' lives, and particularly affected women and vulnerable populations. Conclusion: This scoping review highlights the importance of approaching public health policymaking from a social justice perspective. Such an approach argues for social and public health policies to promote health accounting for its social, economic, political, and commercial determinants.
Keywords: COVID-19; lockdown; pandemic; parenting; review.
Copyright © 2023 Fadda, Melotto, Caiata-Zufferey, Puhan, Frei, Albanese and Camerini.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Strategic Preparedness and Response Plan (SPRP 2021) (2022). Available at: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/WHO-WHE-2021.02 (Accessed March 26, 2022).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources