Association of obesity with headache among US children and adolescents: Evidence from NHANES 1999-2004
- PMID: 36686472
- PMCID: PMC9849580
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1072419
Association of obesity with headache among US children and adolescents: Evidence from NHANES 1999-2004
Abstract
Background: Children and adolescents increasingly commonly suffer from obesity and headache. It has been confirmed that there is an association between obesity and headache in adults; however, evidence of such an association in paediatric populations is still controversial. Therefore, this study examined the relationship between obesity and headache among children and adolescents in the US.
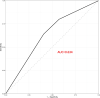
Methods: The cross-sectional data of 3948 participants were obtained from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2004. Weighted logistic regression models were applied to investigate the association between obesity and headache. Subgroup analysis stratified by sex and age was performed to explore the potential difference in the association of paediatric obesity with headache. The performance of paediatric obesity on headache was assessed by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results: The present study involved 3948 participants, of whom 713 (18.1%) had headache. Compared to those without headache, participants with headache tended to be girls and adolescents, have less calcium intake, and have higher levels of body mass index (BMI), C-reactive protein (CRP), serum ferritin and triglycerides (TGs) (all P < 0.05). After fully adjusting for potential confounders, the ORs with 95% CIs for headache were 1.03 (0.58-1.54) and 1.25 (0.68-2.30) for overweight and obese participants in comparison with normal-weight controls, respectively, implying no association of paediatric obesity with headache independent of other potential confounding factors. In addition, although higher odds of headache were noted in girls and adolescents (aged 10-17 years), no statistically significant difference was found across any subgroups. The area under the ROC (AUC) of paediatric obesity on headache was 0.634.
Conclusions: In summary, our study indicated that obesity is not associated with headache among US children and adolescents. Further prospective studies with larger sample size are needed to validate our findings.
Keywords: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES); children and adolescents; cross-sectional study; headache; obesity.
Copyright © 2023 Bu, Zhu, Wang, Lu, Chen and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association Between the Serum Copper Levels and Environmental Tobacco Exposure on the Risk of Overweight and Obesity in Children: a Study Based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 Oct;202(10):4440-4449. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-04037-9. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024. PMID: 38158458
-
Associations between meal and snack frequency and overweight and abdominal obesity in US children and adolescents from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2003-2012.Br J Nutr. 2016 May 28;115(10):1819-29. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516000854. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27001436
-
The association of caffeine intake and prevalence of obesity among children and adolescents: A cross-sectional survey from NHANES 2011-2020 March.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 3;19(6):e0300566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300566. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38829842 Free PMC article.
-
Association between diet quality scores and risk of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Apr 13;23(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-03966-7. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37046233 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and high myopia in children and adolescents: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.PLoS One. 2022 Mar 25;17(3):e0265317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265317. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35333875 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
CGRP Antagonism and Ketogenic Diet in the Treatment of Migraine.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jan 15;60(1):163. doi: 10.3390/medicina60010163. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 38256423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DiPietro L, Mossberg HO, Stunkard AJ. A 40-year history of overweight children in Stockholm: life-time overweight, morbidity, and mortality. Int J Obes Related Metab Disord (1994) 18:585–90. - PubMed
-
- Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, Barry MJ, Caughey AB, Davidson KW, et al. . Behavioral weight loss interventions to prevent obesity-related morbidity and mortality in adults: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. Jama (2018) 320:1163–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.13022 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous