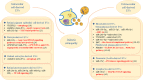
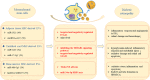
Extracellular vesicles derived from different sources play various roles in diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 36686474
- PMCID: PMC9845915
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1064415
Extracellular vesicles derived from different sources play various roles in diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are present in almost all biological fluids and secreted by almost all cell types. A growing number of studies have revealed the potential roles of EVs in the diagnosis and treatment of the diabetic retinopathy (DR). Changes in the quantity and content of EVs may serve as biomarkers of cause or consequence of pathological status of DR, such as inflammation, neovascularization and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In addition, as natural, safe and efficient drug carrier, EVs have been reported to play important roles in intercellular communication by acting for essential cell-specific information to target cells. In this review, we summarize the roles of EVs, secreted by various types of cells and participated in various biological processes, in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of DR.
Keywords: biomarker; diabetic retinopathy; exosomes; extracellular vesicles (EVs); treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Wang, Wei and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles of human diabetic retinopathy retinal tissue and urine of diabetic retinopathy patients are enriched for the junction plakoglo bin protein.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 6;13:1077644. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1077644. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36686464 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of extracellular vesicles in diabetic retinopathy.Theranostics. 2024 Feb 4;14(4):1631-1646. doi: 10.7150/thno.92463. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 38389842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic Nephropathy: Perspective on Extracellular Vesicles.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 3;11:943. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00943. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in obesity and diabetes mellitus.Mol Aspects Med. 2018 Apr;60:81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 26. Mol Aspects Med. 2018. PMID: 29175307 Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Theranostics.Theranostics. 2017 Sep 26;7(17):4168-4182. doi: 10.7150/thno.21274. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 29158817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell sequencing in diabetic retinopathy: progress and prospects.J Transl Med. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-06066-x. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39806376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of extracellular vesicles for the pathogenesis of retinal diseases: shedding light on blood-retinal barrier dysfunction.J Biomed Sci. 2024 May 10;31(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01036-3. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38730462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles: From large-scale production and engineering to clinical applications.J Tissue Eng. 2025 Apr 30;16:20417314251319474. doi: 10.1177/20417314251319474. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2025. PMID: 40322740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical