Extracellular vesicles derived from different sources play various roles in diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 36686474
- PMCID: PMC9845915
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1064415
Extracellular vesicles derived from different sources play various roles in diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
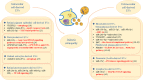
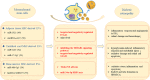
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are present in almost all biological fluids and secreted by almost all cell types. A growing number of studies have revealed the potential roles of EVs in the diagnosis and treatment of the diabetic retinopathy (DR). Changes in the quantity and content of EVs may serve as biomarkers of cause or consequence of pathological status of DR, such as inflammation, neovascularization and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In addition, as natural, safe and efficient drug carrier, EVs have been reported to play important roles in intercellular communication by acting for essential cell-specific information to target cells. In this review, we summarize the roles of EVs, secreted by various types of cells and participated in various biological processes, in the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of DR.
Keywords: biomarker; diabetic retinopathy; exosomes; extracellular vesicles (EVs); treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Chen, Wang, Wei and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical