Language reorganization patterns in global aphasia-evidence from fNIRS
- PMID: 36686505
- PMCID: PMC9853054
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1025384
Language reorganization patterns in global aphasia-evidence from fNIRS
Abstract
Background: Exploring the brain reorganization patterns associated with language recovery would promote the treatment of global aphasia. While functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) has been widely used in the study of speech and language impairment, its application in the field of global aphasia is still limited.
Aims: We aimed to identify cortical activation patterns of patients with global aphasia during naming and repetition tasks.
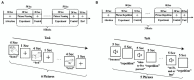
Methods and procedures: We recruited patients with post-stroke aphasia from the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine at Huashan Hospital. These individuals were diagnosed with global aphasia without cognitive impairments, as assessed by speech-language pathology evaluations. Age- and sex-matched healthy controls were recruited from the greater Shanghai area. During fNIRS measurement, patients and healthy controls completed the picture-naming and phrase repetition task. Cortical activation patterns on each of these language tasks were then compared between groups.
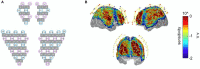
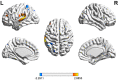
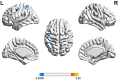
Outcomes and results: A total of nine patients with global aphasia and 14 healthy controls were included in this study. Compared with the healthy subjects, patients with global aphasia showed increased activation in the left Broca's area, middle temporal gyrus (MTG), superior temporal gyrus (STG), and pre-motor and supplementary motor cortex (SMA) (p < 0.05) in the picture-naming task. Furthermore, the latency of the oxyhemoglobin (HbO) concentration in the left supramarginal gyrus (SMG) region had a strong negative correlation with their score of the naming task (p < 0.01). In the phrase repetition task, decreased activation was detected in the left SMA and SMG (p < 0.05) of patients relative to controls.
Conclusion: The left SMG plays a critical role in the language function of patients with global aphasia, especially in their abilities to name and repeat. fNIRS is a promising approach to revealing the changes in brain activities in patients with aphasia, and we believe it will contribute to a deeper understanding of the neurological mechanisms and the establishment of a novel treatment approach for global aphasia.
Keywords: fNIRS; global aphasia; left SMG; picture naming; repetition phrase.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Liu, Tian, Fan, Wang, Qian, Liu, Zhu, Wu and Hu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

