A protocol for the integration of multi-omics bioinformatics: Mechanism of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy for alcohol use disorder
- PMID: 36686540
- PMCID: PMC9849375
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.977487
A protocol for the integration of multi-omics bioinformatics: Mechanism of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy for alcohol use disorder
Abstract
Background: Alcohol use disorder (AUD) has become a significant global factor in various diseases. As a non-pharmacological therapy, certain therapeutic potential has been found in acupuncture; however, in-depth mechanistic studies related to acupuncture for patients with AUD are still insufficient.
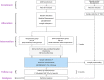
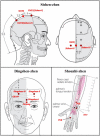
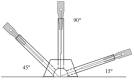
Methods: Based on a randomized control design and a multi-omics analysis plan, this protocol details the recruitment (42 AUD patients), group allocation (21 in acupuncture group vs. 21 in sham acupuncture group), intervention and follow-up (replacement drugs as a normal treatment, 2 weeks acupuncture duration, and 3 month follow-up), and data collection and analytical processes. For the clinical outcomes, in addition to the time required for alcohol withdrawal symptoms to subside as the primary outcome, changes in the alcohol withdrawal symptoms, alcohol craving, mood dysfunction, sleep disorder, fatigue, self-efficacy, gastrointestinal symptoms, the quality of life, and the relapse outcomes will be compared between the groups to confirm the acupuncture clinical effectiveness on alcohol withdraw. The gut microbiome and the fecal metabolomics will also be assessed to explore the association of the structure and the function of gut microflora and the mediation of acupuncture effect on AUD fully utilizing gut microflora multi-modal data and clinical information, via the combination of multi-omics methods, feature screening algorithms and appropriate models.
Discussion: The results of this study may help to strengthen clinical evidence of the mechanism of acupuncture intervention in patients with AUD, through understanding of the regulatory mechanism of acupuncture in the gut microbiome and its metabolism as well as AUD-related clinical manifestations.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry ChiCTR2200058120. Registered on 24 Mar 2022.
Keywords: Jin's three-needle technique; acupuncture; alcohol use disorder; metabolomics; microbiome; multi-modal bioinfomation; multi-omics.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Lan, Fan, Chen, Wei, Li, Fan, Tang and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Forouzanfar MH, Afshin A, Alexander LT, Anderson HR, Bhutta ZA, Biryukov S, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. (2016) 388:1659–724. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murray CJL, Aravkin AY, Zheng P, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abbasi-Kangevari M, et al. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. (2020) 396:1223–49. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30752-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

