Caregiver Burden of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Qualitative Study
- PMID: 36686593
- PMCID: PMC9852954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xkme.2022.100587
Caregiver Burden of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Qualitative Study
Abstract
Rationale & objective: There is limited published research on how autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) impacts caregivers. This study explored how caregivers of individuals with ADPKD perceive the burdens placed on them by the disease.
Study design: Qualitative study consisting of focus groups and interviews. Discussions were conducted by trained interviewers using semi-structured interview guides.
Setting & participants: The research was conducted in 14 countries in North America, South America, Asia, Australia, and Europe. Eligible participants were greater than or equal to 18 years old and caring for a child or adult diagnosed with ADPKD.
Analytical approach: The concepts reported were coded using qualitative research software. Data saturation was reached when subsequent discussions introduced no new key concepts.
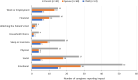
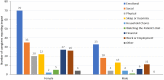
Results: Focus groups and interviews were held with 139 participants (mean age, 44.9 years; 66.9% female), including 25 participants who had a diagnosis of ADPKD themselves. Caregivers reported significant impact on their emotional (74.1%) and social life (38.1%), lost work productivity (26.6%), and reduced sleep (25.2%). Caregivers also reported worry about their financial situation (23.7%). In general, similar frequencies of impact were reported among caregivers with ADPKD versus caregivers without ADPKD, with the exception of sleep (8.0% vs 28.9%, respectively), leisure activities (28.0% vs 40.4% respectively), and work/employment (12.0% vs 29.8%, respectively).
Limitations: The study was observational and designed to elicit concepts, and only descriptive analyses were conducted.
Conclusions: These findings highlight the unique burden on caregivers in ADPKD, which results in substantial emotional, social, and professional/financial impact.
Keywords: Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD); burden; caregiver; quality of life.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polycystic Kidney Disease-Related Disease Burden in Adolescents With Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: An International Qualitative Study.Kidney Med. 2022 Jan 21;4(3):100415. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2022.100415. eCollection 2022 Mar. Kidney Med. 2022. PMID: 35386599 Free PMC article.
-
Pain and Health-Related Quality of Life in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Results from a National Patient-Powered Registry.Kidney Med. 2024 Mar 24;6(5):100813. doi: 10.1016/j.xkme.2024.100813. eCollection 2024 May. Kidney Med. 2024. PMID: 38689835 Free PMC article.
-
Core Outcome Domains for Trials in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: An International Delphi Survey.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Sep;76(3):361-373. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.01.005. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32359822
-
Range and Variability of Outcomes Reported in Randomized Trials Conducted in Patients With Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review.Am J Kidney Dis. 2020 Aug;76(2):213-223. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.12.003. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Am J Kidney Dis. 2020. PMID: 32171640
-
Standardised Outcomes in Nephrology-Polycystic Kidney Disease (SONG-PKD): study protocol for establishing a core outcome set in polycystic kidney disease.Trials. 2017 Nov 23;18(1):560. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2298-4. Trials. 2017. PMID: 29169385 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systematic Scoping Review of Socioeconomic Burden and Associated Psychosocial Impact in Patients With Rare Kidney Diseases and Their Caregivers.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Dec 10;10(3):838-854. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.12.005. eCollection 2025 Mar. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 40225371 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing Meaningful Patient-Centered Outcomes with Relevance for Patients with Polycystic Kidney Disease: Patient, Caregiver, and Researcher Priorities for Research in Polycystic Kidney Disease.Kidney360. 2025 Apr 1;6(4):573-582. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000000695. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Kidney360. 2025. PMID: 39808496 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the concept of caregiver role strain in informal caregivers: an approach according to Meleis.Rev Cuid. 2025 Apr 30;16(1):e4000. doi: 10.15649/cuidarte.4000. eCollection 2025 Jan-Apr. Rev Cuid. 2025. PMID: 40529940 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources