Comprehensive analysis of hypoxia-related genes for prognosis value, immune status, and therapy in osteosarcoma patients
- PMID: 36686667
- PMCID: PMC9853159
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1088732
Comprehensive analysis of hypoxia-related genes for prognosis value, immune status, and therapy in osteosarcoma patients
Abstract
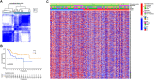
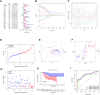
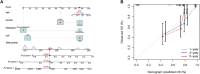
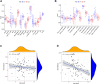
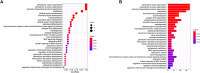
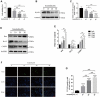
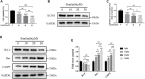
Osteosarcoma is a common malignant bone tumor in children and adolescents. The overall survival of osteosarcoma patients is remarkably poor. Herein, we sought to establish a reliable risk prognostic model to predict the prognosis of osteosarcoma patients. Patients ' RNA expression and corresponding clinical data were downloaded from the Therapeutically Applicable Research to Generate Effective Treatments (TARGET) and Gene Expression Omnibus databases. A consensus clustering was conducted to uncover novel molecular subgroups based on 200 hypoxia-linked genes. A hypoxia-risk models were established by Cox regression analysis coupled with LASSO regression. Functional enrichment analysis, including Gene Ontology annotation and KEGG pathway analysis, were conducted to determine the associated mechanisms. Moreover, we explored relationships between the risk scores and age, gender, tumor microenvironment, and drug sensitivity by correlation analysis. We identified two molecular subgroups with significantly different survival rates and developed a risk model based on 12 genes. Survival analysis indicated that the high-risk osteosarcoma patients likely have a poor prognosis. The area under the curve (AUC) value showed the validity of our risk scoring model, and the nomogram indicates the model's reliability. High-risk patients had lower Tfh cell infiltration and a lower stromal score. We determined the abnormal expression of three prognostic genes in osteosarcoma cells. Sunitinib can promote osteosarcoma cell apoptosis with down-regulation of KCNJ3 expression. In summary, the constructed hypoxia-related risk score model can assist clinicians during clinical practice for osteosarcoma prognosis management. Immune and drug sensitivity analysis can provide essential insights into subsequent mechanisms. KCNJ3 may be a valuable prognostic marker for osteosarcoma development.
Keywords: KCNJ3; chemotherapy; hypoxia; immune microenvironment; osteosarcoma; prognostic model; subtype.
Copyright © 2023 Han, Wu, Zhang, Liang, Xia and Yan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Advances in prognostic models for osteosarcoma risk.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 26;10(7):e28493. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28493. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38586328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of aging/senescence-induced genes in osteosarcoma and predicting clinical prognosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 5;13:997765. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.997765. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275664 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of fatty acid and lactate metabolism-related genes for prognosis value, immune infiltration, and therapy in osteosarcoma patients.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 2;12:934080. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.934080. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36119478 Free PMC article.
-
The hexosamine biosynthesis pathway-related gene signature correlates with immune infiltration and predicts prognosis of patients with osteosarcoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 6;13:1028263. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1028263. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275679 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Hypoxia-Related Subtypes, Establishment of Prognostic Models, and Characteristics of Tumor Microenvironment Infiltration in Colon Cancer.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 17;13:919389. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.919389. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35783281 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Osteopontin derived from hypoxia-induced M2 macrophages promotes osteosarcoma progression through modulation of EGR3/ISG15 signaling and RIG-I expression.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 21;23(1):950. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06936-y. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40841904 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of metastasis-related signatures in osteosarcoma based on tumor microenvironment by integrated bioinformatic analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Dec 19;11(1):e41358. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41358. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39844989 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the Impact of Tumor Microenvironment in Osteosarcoma Progression and Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;15(20):5108. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205108. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in prognostic models for osteosarcoma risk.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 26;10(7):e28493. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28493. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38586328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis reveals the oncogenic role of FoxM1 and its impact on prognosis, immune microenvironment, and drug sensitivity in osteosarcoma.J Appl Genet. 2023 Dec;64(4):779-796. doi: 10.1007/s13353-023-00785-5. Epub 2023 Oct 2. J Appl Genet. 2023. PMID: 37782449
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

