Research progress of abnormal lactate metabolism and lactate modification in immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36686771
- PMCID: PMC9853001
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1063423
Research progress of abnormal lactate metabolism and lactate modification in immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
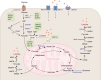
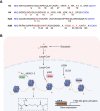
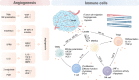
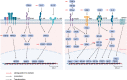
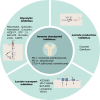
Tumors meet their energy, biosynthesis, and redox demands through metabolic reprogramming. This metabolic abnormality results in elevated levels of metabolites, particularly lactate, in the tumor microenvironment. Immune cell reprogramming and cellular plasticity mediated by lactate and lactylation increase immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment and are emerging as key factors in regulating tumor development, metastasis, and the effectiveness of immunotherapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors. Reprogramming of glucose metabolism and the "Warburg effect" in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) lead to the massive production and accumulation of lactate, so lactate modification in tumor tissue is likely to be abnormal as well. This article reviews the immune regulation of abnormal lactate metabolism and lactate modification in hepatocellular carcinoma and the therapeutic strategy of targeting lactate-immunotherapy, which will help to better guide the medication and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immune regulation; immunotherapy; lactate metabolism; lactylation.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Hao, Ren, Xu, Liu, Song and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

