Crosstalk between protein kinases AKT and ERK1/2 in human lung tumor-derived cell models
- PMID: 36686779
- PMCID: PMC9848735
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1045521
Crosstalk between protein kinases AKT and ERK1/2 in human lung tumor-derived cell models
Abstract
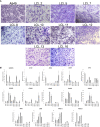
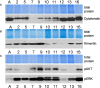
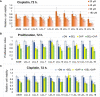
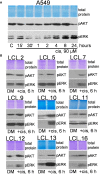
There is no doubt that cell signaling manipulation is a key strategy for anticancer therapy. Furthermore, cell state determines drug response. Thus, establishing the relationship between cell state and therapeutic sensitivity is essential for the development of cancer therapies. In the era of personalized medicine, the use of patient-derived ex vivo cell models is a promising approach in the translation of key research findings into clinics. Here, we were focused on the non-oncogene dependencies of cell resistance to anticancer treatments. Signaling-related mechanisms of response to inhibitors of MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways (regulators of key cellular functions) were investigated using a panel of patients' lung tumor-derived cell lines with various stemness- and EMT-related markers, varying degrees of ERK1/2 and AKT phosphorylation, and response to anticancer treatment. The study of interactions between kinases was the goal of our research. Although MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT interactions are thought to be cell line-specific, where oncogenic mutations have a decisive role, we demonstrated negative feedback loops between MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in all cell lines studied, regardless of genotype and phenotype differences. Our work showed that various and distinct inhibitors of ERK signaling - selumetinib, trametinib, and SCH772984 - increased AKT phosphorylation, and conversely, inhibitors of AKT - capivasertib, idelalisib, and AKT inhibitor VIII - increased ERK phosphorylation in both control and cisplatin-treated cells. Interaction between kinases, however, was dependent on cellular state. The feedback between ERK and AKT was attenuated by the focal adhesion kinase inhibitor PF573228, and in cells grown in suspension, showing the possible role of extracellular contacts in the regulation of crosstalk between kinases. Moreover, studies have shown that the interplay between MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways may be dependent on the strength of the chemotherapeutic stimulus. The study highlights the importance of spatial location of the cells and the strength of the treatment during anticancer therapy.
Keywords: AKT; ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase); cancer cell; cell signaling; cellular resistance; kinase inhibitors; lung cancer; targeted drugs.
Copyright © 2023 Stulpinas, Sereika, Vitkeviciene, Imbrasaite, Krestnikova and Kalvelyte.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Stulpinas A, Imbrasaitė A, Krestnikova N, Valerija Kalvelytė A. Recent approaches encompassing the phenotypic cell heterogeneity for anticancer drug efficacy evaluation. In: Tumor progression and metastasis. London, UK: IntechOpen; (2020). doi: 10.5772/intechopen.89395 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

