Molecular docking/dynamics simulations, MEP analysis, bioisosteric replacement and ADME/T prediction for identification of dual targets inhibitors of Parkinson's disease with novel scaffold
- PMID: 36687301
- PMCID: PMC9852416
- DOI: 10.1007/s40203-023-00139-3
Molecular docking/dynamics simulations, MEP analysis, bioisosteric replacement and ADME/T prediction for identification of dual targets inhibitors of Parkinson's disease with novel scaffold
Abstract
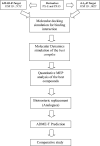
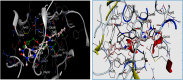
Monoamine oxidase B and Adenosine A2A receptors are used as key targets for Parkinson's disease. Recently, hMAO-B and hA2AR Dual-targets inhibitory potential of a novel series of Phenylxanthine derivatives has been established in experimental findings. Hence, the current study examines the interactions between 38 compounds of this series with hMAO-B and hA2AR targets using different molecular modeling techniques to investigate the binding mode and stability of the formed complexes. A molecular docking study revealed that the compounds L24 ((E)-3-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N-(4-(1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purin-8-yl) phenyl) acrylamide and L32 ((E)-3-(3-Chlorophenyl)-N-(3-(1,3-dimethyl-2,6-dioxo-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-purin-8-yl)phenyl)acrylamide) had a high affinity (S-score: -10.160 and -7.344 kcal/mol) with the pocket of hMAO-B and hA2AR targets respectively, and the stability of the studied complexes was confirmed during MD simulations. Also, the MEP maps of compounds 24 and 32 were used to identify the nucleophilic and electrophilic attack regions. Moreover, the bioisosteric replacement approach was successfully applied to design two new analogs of each compound with similar biological activities and low energy scores. Furthermore, ADME-T and Drug-likeness results revealed the promising pharmacokinetic properties and oral bioavailability of these compounds. Thus, compounds L24, L32, and their analogs can undergo further analysis and optimization in order to design new lead compounds with higher efficacy toward Parkinson's disease.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s40203-023-00139-3.
Keywords: ADME-T; Bioisosteric replacement; MEP maps; Molecular docking/dynamics; Parkinson’s disease; Phenylxanthine derivatives.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures







References
-
- Azam F, Abodabos HS, Taban IM, Rfieda AR, Mahmood D, Anwar MJ, Khan S, Sizochenko N, Poli G, Tuccinardi T, Ali HI. Rutin as promising drug for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: an assessment of MAO-B inhibitory potential by docking, molecular dynamics and DFT studies. Mol Simul. 2019;45(18):1563–1571. doi: 10.1080/08927022.2019.1662003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

