SARS-CoV-2 N protein mediates intercellular nucleic acid dispersion, a feature reduced in Omicron
- PMID: 36687314
- PMCID: PMC9841735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.105995
SARS-CoV-2 N protein mediates intercellular nucleic acid dispersion, a feature reduced in Omicron
Abstract
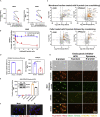
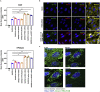
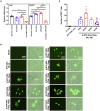
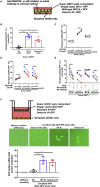
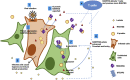
The coronavirus nucleocapsid (N) protein is known to bind to nucleic acids and facilitate viral genome encapsulation. Here we report that the N protein can mediate RNA or DNA entering neighboring cells through ACE2-independent, receptor (STEAP2)-mediated endocytosis, and achieve gene expression. The effect is more pronounced for the N protein of wild-type SARS-CoV-2 than that of the Omicron variant and other human coronaviruses. This effect is enhanced by RANTES (CCL5), a chemokine induced by N protein, and lactate, a metabolite produced in hypoxia, to cause more damage. These findings might explain the clinical observations in SARS-CoV-2-infected cases. Moreover, the N protein-mediated function can be inhibited by N protein-specific monoclonal antibodies or p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors. Since the N-protein-mediated nucleic acid endocytosis involves a receptor commonly expressed in many types of cells, our findings suggest that N protein may have an additional role in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis.
Keywords: Molecular biology; Virology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Chan J.F.W., Kok K.H., Zhu Z., Chu H., To K.K.W., Yuan S., Yuen K.Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020;9:221–236. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

