E, K, B5, B6, and B9 vitamins and their specific immunological effects evaluated by flow cytometry
- PMID: 36687400
- PMCID: PMC9849766
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1089476
E, K, B5, B6, and B9 vitamins and their specific immunological effects evaluated by flow cytometry
Abstract
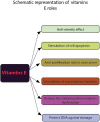
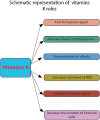
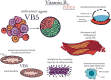
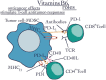
It has been proven that vitamins play an essential role in preventing certain diseases since ancient times. It is thus fruitless to approach the roles of vitamins without making reference to the techniques used in evaluating the effects of these micronutrients. Therefore, the aim of this paper was to summarize the immunological effects of E, K, B5, B6, and B9 vitamins evaluated by flow cytometry. Some of these significant effects were presented and discussed: (a) The role of vitamins E in the prevention and treatment of different types of cancer. (b) The properties of K vitamins in the development and maintenance of pheochromocytoma Cell Line 12 (PC12) cells in Parkinson's disease; (c) The improvement effect of vitamin B5 on the loss of bone mass in low estrogen conditions; (d) The anticancer role of vitamins B6. (e) The role of Vitamin B9 in the regulation of Treg cells. As such, the flow cytometry technique used to assess these properties is essential to evaluate the immunomodulatory effects of certain vitamins. The technique undergoes constant improvement which makes it possible to determine several parameters with a role in the modulation of the immune function and at the same time increase the accuracy of the methods that highlight them.
Keywords: anticancer; diseases; flow cytometry; immunology; vitamins.
Copyright © 2023 Munteanu, Berindean, Mihai, Pop, Popa, Muntean, Petrescu and Ona.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

