Association of cardiac calcium burden with overall survival after radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 36687507
- PMCID: PMC9852638
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phro.2023.01.001
Association of cardiac calcium burden with overall survival after radiotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background and purpose: Coronary calcifications are associated with coronary artery disease in patients undergoing radiotherapy (RT) for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We quantified calcifications in the coronary arteries and aorta and investigated their relationship with overall survival (OS) in patients treated with definitive RT (Def-RT) or post-operative RT (PORT).
Materials and methods: We analyzed 263 NSCLC patients treated from 2004 to 2017. Calcium burden was ascertained with a Hounsfield unit (HU) cutoff of > 130 in addition to a deep learning (DL) plaque estimator. The HU cutoff volumes were defined for coronary arteries (PlaqueCoro) and coronary arteries and aorta combined (PlaqueCoro+Ao), while the DL estimator ranged from 0 (no plaque) to 3 (high plaque). Patient and treatment characteristics were explored for association with OS.
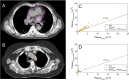
Results: The median PlaqueCoro and PlaqueCoro+Ao was 0.75 cm3 and 0.87 cm3 in the Def-RT group and 0.03 cm3 and 0.52 cm3 in the PORT group. The median DL estimator was 2 in both cohorts. In Def-RT, large PlaqueCoro (HR:1.11 (95%CI:1.04-1.19); p = 0.008), and PlaqueCoro+Ao (HR:1.06 (95%CI:1.02-1.11); p = 0.03), and poor Karnofsky Performance Status (HR: 0.97 (95%CI: 0.94-0.99); p = 0.03) were associated with worse OS. No relationship was identified between the plaque volumes and OS in PORT, or between the DL plaque estimator and OS in either Def-RT or PORT.
Conclusions: Coronary artery calcification assessed from RT planning CT scans was significantly associated with OS in patients who underwent Def-RT for NSCLC. This HU thresholding method can be straightforwardly implemented such that the role of calcifications can be further explored.
Keywords: Coronary calcifications; Non-small cell lung cancer; Radiotherapy.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiotherapy-related lymphopenia in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving palliative radiotherapy.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020 Feb 19;22:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2020.02.005. eCollection 2020 May. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32181373 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary Artery Calcifications and Cardiac Risk After Radiation Therapy for Stage III Lung Cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Jan 1;112(1):188-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2021.08.017. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 34419565 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac dose is associated with immunosuppression and poor survival in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Sep;128(3):498-504. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 May 30. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29859754
-
The efficacy of postoperative radiotherapy for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cancer Res Ther. 2022 Dec;18(7):1910-1918. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_167_22. J Cancer Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36647949
-
Modern post-operative radiotherapy for stage III non-small cell lung cancer may improve local control and survival: a meta-analysis.Radiother Oncol. 2014 Jan;110(1):3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.08.011. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Radiother Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24100149 Review.
Cited by
-
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockers improve survival in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer combined with hypertension undergoing radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 28;15(1):10702. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93205-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40155651 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac substructure delineation in radiation therapy - A state-of-the-art review.J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024 Dec;68(8):914-949. doi: 10.1111/1754-9485.13668. Epub 2024 May 17. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38757728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bradley J.D., Paulus R., Komaki R., Masters G., Blumenschein G., Schild S., et al. Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): a randomised, two-by-two factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:187–199. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71207-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bradley J.D., Hu C., Komaki R.R., Masters G.A., Blumenschein G.R., Schild S.E., et al. Long-term results of NRG Oncology RTOG 0617: standard- versus high-dose chemoradiotherapy with or without cetuximab for unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:706–714. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.01162. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

