Beta-Blockers for Primary Prevention of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiac Toxicity: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
- PMID: 36687509
- PMCID: PMC9818032
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8367444
Beta-Blockers for Primary Prevention of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiac Toxicity: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials
Abstract
Aim: Cardiotoxicity is a well-recognized complication of chemotherapy with Anthracyclines. However, results from trials evaluating beta-blockers for prevention are controversial. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis to find whether prophylactic administration of beta-blockers can help prevent Anthracyclines-induced cardiotoxicity.
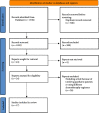
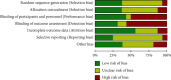
Methods: We assessed randomized trials and observational studies where a prophylactic intervention was compared with a control arm in patients with a normal left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) receiving Anthracyclines. The primary outcome was EF reduction. The secondary outcome was the development of Cancer Therapeutics-Related Cardiac Dysfunction (CTRCD), defined as a decrease in the LVEF of >10% to a value of <53%.
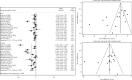
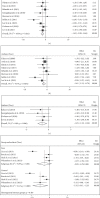
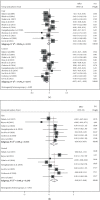
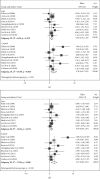
Results: We included 17 trials comprising 1291 patients (671 patients in the intervention arm and 620 in the control arm). Carvedilol was administered in eight studies, and others used bisoprolol, metoprolol, or nebivolol. Compared with baseline, LVEF reduced in both intervention and control groups after chemotherapy (MD = -1.93%, 95% CI: -2.94, -0.92, p = 0.001, I2 = 72.1% vs. MD = -4.78%, 95% CI: -6.51, -3.04, p = 0.001, I 2 = 91.6%, respectively). LVEF was less reduced among the beta-blocker receivers (MD = 3.44%, 95% CI: 1.41-5.46, p = 0.001, I2 = 94.0%). Among the eight studies reporting the incidence of CTRCD, 45 out of 370 participants in the intervention arm and 54 out of 341 in the control arm were reported to experience this complication (RR = 0.76; 95% CI: 0.53,1.09; I 2 = 24.4%; p = 0.235).
Conclusion: Treatment with beta-blockers prevents dilatation of the left ventricle, development of diastolic dysfunction, and reduction of LVEF. However, these hemodynamic effects do not translate into a significant reduction in CTRCD incidence and prevention of hospitalization for heart failure or cardiac death.
Copyright © 2022 Armin Attar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beta-blockers for the primary prevention of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Apr 25;20(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40360-019-0298-6. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31023386 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Effects and Duration of Beta Blocker Therapy in Anthracycline-Treated Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020 Feb;20(1):11-19. doi: 10.1007/s12012-019-09558-1. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31832905
-
Statins to prevent early cardiac dysfunction in cancer patients at increased cardiotoxicity risk receiving anthracyclines.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2023 Sep 20;9(6):515-525. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvad031. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37120736 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of beta-blockers and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors for preventing left ventricular dysfunction due to anthracyclines or trastuzumab in patients with breast cancer.Eur Heart J. 2022 Jul 14;43(27):2562-2569. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab843. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 34951629
-
Rationale and Design of the Cardiac CARE Trial: A Randomized Trial of Troponin-Guided Neurohormonal Blockade for the Prevention of Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity.Circ Heart Fail. 2022 Jul;15(7):e009445. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.009445. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Circ Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35766037 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer-Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction: Latest Advances in Prevention and Treatment.Life (Basel). 2025 Mar 15;15(3):471. doi: 10.3390/life15030471. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40141815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular Considerations During Cancer Therapy: Gaps in Evidence and JACC: CardioOncology Expert Panel Recommendations.JACC CardioOncol. 2024 Nov 5;6(6):815-834. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2024.06.005. eCollection 2024 Dec. JACC CardioOncol. 2024. PMID: 39801647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotective strategies in the management of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: current approaches and future directions.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Oct 16;86(12):7212-7220. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000002668. eCollection 2024 Dec. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39649884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGLT2i and Primary Prevention of Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction in Patients With Diabetes.JACC CardioOncol. 2024 Sep 22;6(6):863-875. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2024.08.001. eCollection 2024 Dec. JACC CardioOncol. 2024. PMID: 39801650 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

