LGBMDF: A cascade forest framework with LightGBM for predicting drug-target interactions
- PMID: 36687573
- PMCID: PMC9849804
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1092467
LGBMDF: A cascade forest framework with LightGBM for predicting drug-target interactions
Abstract
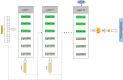
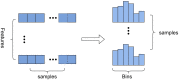
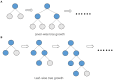
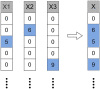
Prediction of drug-target interactions (DTIs) plays an important role in drug development. However, traditional laboratory methods to determine DTIs require a lot of time and capital costs. In recent years, many studies have shown that using machine learning methods to predict DTIs can speed up the drug development process and reduce capital costs. An excellent DTI prediction method should have both high prediction accuracy and low computational cost. In this study, we noticed that the previous research based on deep forests used XGBoost as the estimator in the cascade, we applied LightGBM instead of XGBoost to the cascade forest as the estimator, then the estimator group was determined experimentally as three LightGBMs and three ExtraTrees, this new model is called LGBMDF. We conducted 5-fold cross-validation on LGBMDF and other state-of-the-art methods using the same dataset, and compared their Sn, Sp, MCC, AUC and AUPR. Finally, we found that our method has better performance and faster calculation speed.
Keywords: LightGBM; deep forest; drug-target interactions; machine learning; prediction.
Copyright © 2023 Peng, Zhao, Zeng, Hu and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DeepStack-DTIs: Predicting Drug-Target Interactions Using LightGBM Feature Selection and Deep-Stacked Ensemble Classifier.Interdiscip Sci. 2022 Jun;14(2):311-330. doi: 10.1007/s12539-021-00488-7. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Interdiscip Sci. 2022. PMID: 34731411
-
DTI-CDF: a cascade deep forest model towards the prediction of drug-target interactions based on hybrid features.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jan 18;22(1):451-462. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz152. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 31885041
-
DDR: efficient computational method to predict drug-target interactions using graph mining and machine learning approaches.Bioinformatics. 2018 Apr 1;34(7):1164-1173. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx731. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29186331 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of network-based approaches and machine learning algorithms for predicting drug-target interactions.Methods. 2022 Feb;198:19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.10.007. Epub 2021 Nov 1. Methods. 2022. PMID: 34737033 Review.
-
Deep Learning in Drug Target Interaction Prediction: Current and Future Perspectives.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(11):2100-2113. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200907141016. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32895036 Review.
Cited by
-
ISLRWR: A network diffusion algorithm for drug-target interactions prediction.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 30;20(1):e0302281. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302281. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39883675 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-target interaction prediction through fine-grained selection and bidirectional random walk methodology.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 5;14(1):18104. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69186-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39103483 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning and radiomics for predicting efficacy of programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor for small cell lung cancer: A multicenter cohort study.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Jun;14(6):e1673. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1673. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38840331 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Machine learning to predict the occurrence of thyroid nodules: towards a quantitative approach for judicious utilization of thyroid ultrasonography.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 7;15:1385836. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1385836. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38774231 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of miRNA-disease association based on multisource inductive matrix completion.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 11;14(1):27503. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78212-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39528650 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

