A research program-linked, course-based undergraduate research experience that allows undergraduates to participate in current research on mycobacterial gene regulation
- PMID: 36687599
- PMCID: PMC9853274
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1025250
A research program-linked, course-based undergraduate research experience that allows undergraduates to participate in current research on mycobacterial gene regulation
Abstract
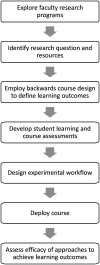
Undergraduate instructional biology laboratories are typically taught within two paradigms. Some labs focus on protocols and techniques delivered in "cookbook" format with defined experimental outcomes. There is increasing momentum to alternatively employ student-driven, open-ended, and discovery-based strategies, often via course-based undergraduate research experiences (CUREs) using crowd-sourcing initiatives. A fraction of students also participate in funded research in faculty research labs, where they have opportunities to work on projects designed to expand the frontiers of human knowledge. These experiences are widely recognized as valuable but are not scalable, as most institutions have many more undergraduates than research lab positions. We sought to address this gap through our department's curriculum by creating an opportunity for students to participate in the real-world research process within a laboratory course. We conceived, developed, and delivered an authentic, guided research experience to students in an upper-level molecular biology laboratory course. We refer to this model as a "research program-linked CURE." The research questions come directly from a faculty member's research lab and evolve along with that research program. Students study post-transcriptional regulation in mycobacteria. We use current molecular biology methodologies to test hypotheses like "UTRs affect RNA and protein expression levels," "there is functional redundancy among RNA helicases," and "carbon starvation alters mRNA 5' end chemistries." We conducted standard assessments and developed a customized "Skills and Concepts Inventory" survey to gauge how well the course met our student learning outcomes. We report the results of our assessments and describe challenges addressed during development and execution of the course, including organizing activities to fit within an instructional lab, balancing breadth with depth, and maintaining authenticity while giving students the experience of obtaining interpretable and novel results. Our data suggest student learning was enhanced through this truly authentic research approach. Further, students were able to perceive they were participants and contributors within an active research paradigm. Students reported increases in their self-identification as scientists, and a positive impact on their career trajectories. An additional benefit was reciprocation back to the funded research laboratory, by funneling course alumni, results, materials, and protocols.
Keywords: CRISPRi; Mycolicibacterium smegmatis; RNA; assessments; authentic research; gene expression; molecular biology; undergraduate laboratory teaching.
Copyright © 2023 Roberts and Shell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
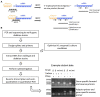
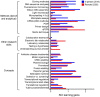
References
-
- Benchling Biology Software . (2022). Available at: benchling.com (Accessed August 21, 2022).
-
- Brewer C., Smith D., eds. (2011). Vision and Change in Undergraduate Biology Education: A Call to Action. Washington, DC: American Association for the Advancement of Science.
-
- Buckholt M. A., Roberts L. A., Whitefleet-Smith J. A., Rulfs J. (2022). Redesigning undergraduate labs: from recipes to research. Afr. J. Inter Multidiscip. Stud. Accepted for Publication. (in press)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

