Fosthiazate inhibits root-knot disease and alters rhizosphere microbiome of Cucumis melo var. saccharinus
- PMID: 36687623
- PMCID: PMC9853079
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1084010
Fosthiazate inhibits root-knot disease and alters rhizosphere microbiome of Cucumis melo var. saccharinus
Abstract
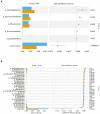
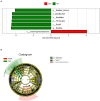
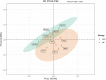
Root-knot nematodes especially Meloidogyne spp. are considered as most destructive obligate parasites that substantially reduce crop yield and quality. Fosthiazate is an efficient organothiophosphate chemical with nematicidal activity against Meloidogyne spp. The present study aimed to analyze the efficacy of fosthiazate against root-knot disease in Cucumis melo var. saccharinus and its potential effects on rhizosphere microbiome and metabolites. The fosthiazate (40%) was applied two times by spraying on the day of transplanting and during the pollination period (after 31 days). Samples from treatment (fosthiazate 40%: MF) and control groups (untreated plants; MCK) were analysed through metagenomic and metabolomic profiling of rhizospheres. Results revealed that root-knot index of the MF group (9.26 ± 1.28) was significantly (p < 0.05) lower than the MCK group (22.06 ± 0.71) with a control effect of 57.85% after 31 days of the first spray, whereas fosthiazate efficacy reduced to 31.87% after 38 days of second application with significantly (p < 0.05) different root-knot index values (MF: 56 ± 1.43 and; MCK: 82.26 ± 3.87). However, Cucumis melo var. saccharinus fruit yield in both groups (MCK: 21.1 ± 0.9 and MF: 21.53 ± 0.85) showed no differences (p > 0.05). Metagenomic profiling revealed Proteobacteria, Acidobacteriota, and Firmicutes as predominant phyla and Bacillus, Sphingomonas, and Acidibacter as predominant genera in rhizosphere soil samples of both MF and MCK groups. Further, a t-test revealed higher differential enrichment of Firmicutes at phylum level and Bacillus at genus level in MF than MCK. Metabolomic profiling of rhizospheric soil revealed a total of six differential metabolites (p < 0.05), four of them (Sucrose, Hexaonic acid 1, (Z)-9-Octadecenamide 1, and Hexadecanamide) were up-regulated in MF group, whereas two of them (2,3,4-Trihydroxy-3-(Hydroxymethyl) Butanol and Sulfurous acid, 2, ethylhexylundecyl ester) were down-regulated in CK group. Our study concluded that fosthiazate exhibits a better control over the rook-knot disease in the short term and resulted in trackable changes in rhizosphere microbiome and metabolome.
Keywords: Cucumis melo var. saccharinus; Meloidogyne; bacterial diversity; fosthiazate; metabolomic profiling; root-knot disease.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Yan, Luo, Zeng, Zhao, Dou and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
First Report of Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne incognita on Olea europaea in the Republic of Korea.Plant Dis. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-05-25-1024-PDN. Online ahead of print. Plant Dis. 2025. PMID: 40579837
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
Cited by
-
GPCR Sense Communication Among Interaction Nematodes with Other Organisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 20;26(6):2822. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062822. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141464 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelkhalik A., Pascual-Seva N., Nájera I., Giner A., Baixauli C., Pascual B. (2019). Yield response of seedless watermelon to different drip irrigation strategies under Mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 212, 99–110. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2018.08.044 - DOI
-
- Adetunji C. O., Oloke J. K., Bello O. M., Pradeep M., Jolly R. S. (2019). Isolation, structural elucidation and bioherbicidal activity of an eco-friendly bioactive 2-(Hydroxymethyl) phenol, from pseudomonas Aeruginosa (C1501) and its Ecotoxicological evaluation on soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 13, 304–317. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2018.12.006 - DOI
-
- Al-Daghari D. S. S., Al-Sadi A. M., Velazhahan R. (2020). Monosporascus root rot and vine decline disease of muskmelon (Cucumis Melo l.): An overview. Trop. Agric. 98, 406–418.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

