Microbial metabolites indole derivatives sensitize mice to D-GalN/LPS induced-acute liver failure via the Tlr2/NF-κB pathway
- PMID: 36687651
- PMCID: PMC9852867
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1103998
Microbial metabolites indole derivatives sensitize mice to D-GalN/LPS induced-acute liver failure via the Tlr2/NF-κB pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Acute liver failure (ALF) is a clinical condition with many causes, fast progression, and a poor prognosis. Previous research has indicated that microbial factors have a role in ALF, but a clear picture has yet to emerge.
Methods: To investigate the specific involvement of microbial metabolites in ALF development, we pretreated D-GalN/LPS-induced ALF mice with indole derivatives, an influential class of gut microbial metabolites.
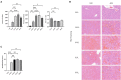
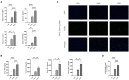
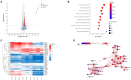
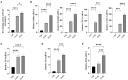
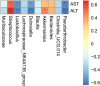
Results: Contrary to their typical role as anti-inflammatory agents in the host, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), indole-3-lactic acid (ILA), and indolepropionic acid (IPA) gavage sensitize mice to D-GalN/LPS-induced-ALF with a rapid rise in serum transaminases and histologic lesion. For a clearer picture, we performed comprehensive analysis for the IAA therapy. IAA markedly amplified inflammatory response and cellular damage. The transcriptome analysis indicated the participation of the TNF-α/NF-κB signaling pathway. The structure of gut microbiota in ileum and the expression of Toll-like receptor 2 (Tlr2) in the liver were also significantly changed.
Discussion: In conclusion, IAA pretreatment can exacerbate D-GalN/LPS-induced ALF via probable Tlr2/NF-κB pathway involvement and ileac dysbiosis characterized by enriched gram-positive genus with potential pathogenesis. Microbial metabolites IAA may aggravate individual susceptibility to D-GalN/LPS-induced ALF. Further investigation of the underlying mechanism is needed, and intervention with indole derivatives and related commensal species should be undertaken with caution.
Keywords: NF-κB; acute liver failure; gut microbiota; indole derivatives; microbial metabolites; toll-like receptor 2.
Copyright © 2023 Zhou, Wang, Pan, Lv, Lou, Han, Yao, Chen, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

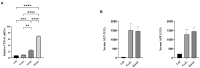
Similar articles
-
UMSCs Attenuate LPS/D-GalN-induced Acute Liver Failure in Mice by Down-regulating the MyD88/NF-κB Pathway.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021 Oct 28;9(5):690-701. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00157. Epub 2021 Apr 22. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34722184 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of 4-Octyl Itaconate in Murine LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Failure via Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Aug 17;2021:9932099. doi: 10.1155/2021/9932099. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34457120 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of sea buckthorn polysaccharide extracts against LPS/d-GalN-induced acute liver failure in mice via suppressing TLR4-NF-κB signaling.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.029. Epub 2015 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26494508
-
The Key Molecular Mechanisms of Sini Decoction Plus Ginseng Soup to Rescue Acute Liver Failure: Regulating PPARα to Reduce Hepatocyte Necroptosis?J Inflamm Res. 2022 Aug 22;15:4763-4784. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S373903. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36032938 Free PMC article.
-
Current progress on the microbial therapies for acute liver failure.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 16;15:1452663. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1452663. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39479215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Indole-3-Lactic Acid Inhibits Doxorubicin-Induced Ferroptosis Through Activating Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor/Nrf2 Signalling Pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jan;29(2):e70358. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70358. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39854052 Free PMC article.
-
Calycosin inhibits hepatocyte apoptosis in acute liver failure by suppressing the TLR4/NF-κB pathway: An in vitro study.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Jul;11(7):e935. doi: 10.1002/iid3.935. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. Retraction in: Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025 Jul;13(7):e70234. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70234. PMID: 37506138 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Crosstalk between lactic acid and immune regulation and its value in the diagnosis and treatment of liver failure.Open Life Sci. 2023 Sep 11;18(1):20220636. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0636. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37724112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted Role of Microbiota-Derived Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Human Diseases and Its Potential Clinical Application.FASEB J. 2025 Jun 15;39(11):e70574. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500295R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40415505 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

