Evaluate how steaming and sulfur fumigation change the microstructure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of Gastrodia elata Bl. starch
- PMID: 36687729
- PMCID: PMC9849879
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1087453
Evaluate how steaming and sulfur fumigation change the microstructure, physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of Gastrodia elata Bl. starch
Abstract
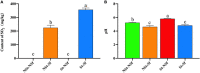
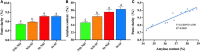
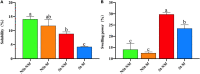
The sulfur dioxide gas (SO2) generated by sulfur burning can improve the appearance quality of food and enhance the storage time. However, excessive sulfur dioxide will pollute the environment and cause deterioration of food quality, and even the high residual levels can increase the risk of cancer. As Gastrodia elata Blume is prone to corruption during processing, sulfur fumigation is often used for preservation. In this study, spectral analysis and Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) were used to investigate the effects of traditional sulfur fumigation processing on the morphology quality, edible quality and structural characteristics of G. elata. The results showed that compared with direct drying, the pH decreased by 0.399 of the sulfur fumigated after steamed treatment G. elata, and the morphology quality, pasting ability and gel edible quality of the starch were significantly improved. In addition, it was suggested that sulfur fumigation after steaming could promote the release of molecular chains from starch granules and thus enhance the cross-linking between molecules, which explained the reason for the improve of starch edible quality. This study can provide technical and theoretical support for improving the quality of starch rich foods, replacing sulfur fumigation and reducing potential environmental hazards.
Keywords: Gastrodia elata starch; edible quality; steaming; sulfur dioxide gas; sulfur fumigation.
Copyright © 2023 Guan, Chen, Guo, Cui, Xu, Wan, Zhou, Wang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Selection and application of aptamers for p-hydroxybenzyl hydrogen sulfite after Gastrodia elata Bl. fumigated with sulfur.Talanta. 2024 Mar 1;269:125461. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.125461. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Talanta. 2024. PMID: 38056416
-
A practical protocol for comprehensive evaluation of sulfur-fumigation of Gastrodia Rhizoma using metabolome and health risk assessment analysis.J Hazard Mater. 2017 Oct 15;340:221-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Jul 4. J Hazard Mater. 2017. PMID: 28715745
-
How steaming and drying processes affect the active compounds and antioxidant types of Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. chow.Food Res Int. 2022 Jul;157:111277. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111277. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35761588
-
A Review of Gastrodia Elata Bl.: Extraction, Analysis and Application of Functional Food.Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024 Sep 27:1-30. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2024.2397994. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Anal Chem. 2024. PMID: 39355975 Review.
-
The rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume - An ethnopharmacological review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 2;189:361-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.057. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27377337 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Steam and Water Blanching on Drying Characteristics, Water Distribution, Microstructure, and Bioactive Components of Gastrodia Elata.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 20;12(6):1372. doi: 10.3390/plants12061372. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36987061 Free PMC article.
-
Drying kinetics and characteristics of Acori tatarinowii rhizoma under hot air thin-layer drying at different temperatures.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;15(1):30447. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13497-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40830622 Free PMC article.
-
Application for Identifying the Origin and Predicting the Physiologically Active Ingredient Contents of Gastrodia elata Blume Using Visible-Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning.Foods. 2023 Nov 8;12(22):4061. doi: 10.3390/foods12224061. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38002117 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Maintains Postharvest Quality in Fresh Gastrodia elata Tuber by Regulating Antioxidant Ability and Phenylpropanoid and Energy Metabolism During Storage.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 1;25(21):11752. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111752. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519304 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of steam cooking on the chemical profile of table-stock sweetpotatoes with different carotenoids content.Food Chem X. 2024 Mar 19;22:101308. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101308. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Food Chem X. 2024. PMID: 38550893 Free PMC article.
References
-
- NHFPC National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Chinese National Standard for the Use of Food Additives (GB2076–2014). Beijing: NHFPC; (2014).
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing: Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission; (2020).
-
- Li Y, Shabani KI, Liu HB, Guo Q, Liu X. Structural, physicochemical and rheological properties of a novel native starch obtained from Rhizoma Gastrodiae. Food Struct. (2020) 25:100148. 10.1016/j.foostr.2020.100148 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

