Latilactobacillus sakei Furu2019 and stachyose as probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics alleviate constipation in mice
- PMID: 36687730
- PMCID: PMC9849682
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1039403
Latilactobacillus sakei Furu2019 and stachyose as probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics alleviate constipation in mice
Abstract
Introduction: Slow transit constipation (STC) is a common disorder in the digestive system. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of stachyose (ST) and Latilactobacillus sakei Furu 2019 (L. sakei) alone or combined on diphenoxylate-induced constipation and explore the underlying mechanisms using a mouse model.
Methods: ICR mice were randomly divided into five groups. The normal and constipation model groups were intragastrically administrated with PBS. The ST, L. sakei, and synbiotic groups were intragastrically administrated with ST (1.5 g/kg body weight), alive L. sakei (3 × 109 CFU/mouse), or ST + L. sakei (1.5 g/kg plus 3 × 109 CFU/mouse), respectively. After 21 days of intervention, all mice except the normal mice were intragastrically administrated with diphenoxylate (10 mg/kg body weight). Defecation indexes, constipation-related intestinal factors, serum neurotransmitters, hormone levels, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), and intestinal microbiota were measured.
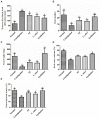
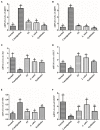
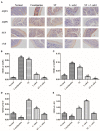
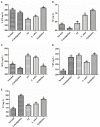
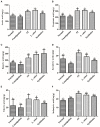
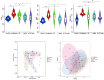
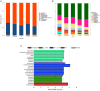
Results: Our results showed that three interventions with ST, L. sakei, and synbiotic combination (ST + L. sakei) all alleviated constipation, and synbiotic intervention was superior to ST or L. sakei alone in some defecation indicators. The RT-PCR and immunohistochemical experiment showed that all three interventions relieved constipation by affecting aquaporins (AQP4 and AQP8), interstitial cells of Cajal (SCF and c-Kit), glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS). The three interventions exhibited a different ability to increase the serum excitatory neurotransmitters and hormones (5-hydroxytryptamine, substance P, motilin), and reduce the serum inhibitory neurotransmitters (vasoactive intestinal peptide, endothelin). The result of 16S rDNA sequencing of feces showed that synbiotic intervention significantly increased the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria such as Akkermansia, and regulated the gut microbes of STC mice. In conclusion, oral administration of ST or L. sakei alone or combined are all effective to relieve constipation and the symbiotic use may have a promising preventive effect on STC.
Keywords: Latilactobacillus sakei; intestinal flora; slow transit constipation; stachyose; synbiotics.
Copyright © 2023 Guo, Song, Huang, Li, Xiao, Wang and Ren.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum GUANKE on Diphenoxylate-Induced Slow Transit Constipation and Gut Microbiota in Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 26;15(17):3741. doi: 10.3390/nu15173741. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686774 Free PMC article.
-
Synbiotic yogurt containing konjac mannan oligosaccharides and Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. lactis BB12 alleviates constipation in mice by modulating the stem cell factor (SCF)/c-Kit pathway and gut microbiota.J Dairy Sci. 2021 May;104(5):5239-5255. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19449. Epub 2021 Mar 2. J Dairy Sci. 2021. PMID: 33663840
-
Ameliorative effects of the mixed aqueous extract of Aurantii Fructus Immaturus and Magnoliae Officinalis Cortex on loperamide-induced STC mice.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(13):e33705. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33705. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39040398 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics in chronic constipation: Outstanding aspects to be considered for the current evidence.Front Nutr. 2022 Dec 8;9:935830. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.935830. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36570175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Latilactobacillus sakei: a candidate probiotic with a key role in food fermentations and health promotion.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(4):978-995. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2111402. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 35997270 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum GUANKE on Diphenoxylate-Induced Slow Transit Constipation and Gut Microbiota in Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Aug 26;15(17):3741. doi: 10.3390/nu15173741. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37686774 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Influence of Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on the Human Gut Microbiome and Intestinal Integrity.J Clin Med. 2025 May 23;14(11):3673. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113673. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactobacillus rhamnosus Glory LG12 preventives loperamide-induced constipation in mice by modulating intestinal flora and metabolic pathways.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 11;16:1577799. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1577799. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40718808 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Fiber as Prebiotics: A Mitigation Strategy for Metabolic Diseases.Foods. 2025 Jul 29;14(15):2670. doi: 10.3390/foods14152670. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40807605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Yeast Strain YA176 for Bio-Purification of Soy Molasses to Produce Raffinose Family Oligosaccharides and Optimization of Fermentation Conditions.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Feb;197(2):943-963. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05065-4. Epub 2024 Sep 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39340630
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

