Conversion of One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is Effective in Dealing with Late Complications of OAGB: Experience from a Tertiary Bariatric Center and Literature Review
- PMID: 36687754
- PMCID: PMC9847651
- DOI: 10.17476/jmbs.2021.10.1.32
Conversion of One-Anastomosis Gastric Bypass (OAGB) to Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) is Effective in Dealing with Late Complications of OAGB: Experience from a Tertiary Bariatric Center and Literature Review
Abstract
Purpose: Both primary and revisional bariatric surgery are on the rise due to global obesity pandemic. This study aimed to assess the indications for revision after one-anastomosis gastric bypass (OAGB) and the outcomes after laparoscopic conversion of OAGB to roux-en-y gastric bypass (RYGB).
Materials and methods: Retrospective review on patients that had undergone conversion of OAGB to RYGB between June 2007-June 2019 in a tertiary bariatric center, followed by literature review.
Results: Out of 386 revisional bariatric surgery, a total of 14 patients underwent laparoscopic conversion of OAGB to RYGB. The mean age was 44.7 with 71% female. The mean pre-revision BMI was 29.2 kg/m2. The primary indications for revision were bile reflux (n=7), marginal ulcer (n=3), inadequate weight loss or weight regain (IWL/WR) (n=3) and protein-calorie malnutrition (n=1). Conversion of OAGB to RYGB was completed laparoscopically in all cases. The mean length of stay was 4.1 days. There was no intraoperative or early post-operative complication. The mean total weight loss (rTWL%) after revision at year one, year three and year five post-revision were 11.5%, 18.1% and 29.1%, respectively. All patients achieved resolution of bile reflux and marginal ulcer. There was no mortality in this cohort.
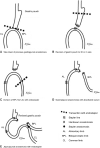
Conclusion: Bile reflux, marginal ulcer, IWL/WR and malnutrition were the main indications for revision after OAGB in this study. In concordance with the available evidence, laparoscopic conversion of OAGB to RYGB was safe and effective in dealing with late complications of OAGB.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Gastric bypass; Outcomes; Revision.
Copyright © 2021, The Korean Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO factsheet. Obesity and overweight [Internet] Geneva: WHO; 2020. [cited 2021 Jan 30]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- Sjöström L. Review of the key results from the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) trial - a prospective controlled intervention study of bariatric surgery. J Intern Med. 2013;273:219–234. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials