Music therapy effect on anxiety reduction among patients with cancer: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 36687940
- PMCID: PMC9853974
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1028934
Music therapy effect on anxiety reduction among patients with cancer: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: The study aimed to investigate the effect of music therapy on anxiety alleviation among cancer patients.
Methods: A comprehensive literature research was performed in four electronic databases (PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science). Fifteen randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included. The risk of bias for the RCTs was evaluated by the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool. Anxiety levels were extracted to synthesize the combined effect by using meta-analysis. All analyses were performed using R version 4.0.4.
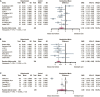
Results: In total, 15 RCTs met the inclusion criteria involving 1320 cancer patients (662 patients in the experimental group and 658 patients in the controlled group). The majority of interventions were performed with recorded music lasting for 15-60 minutes. Compared with standard care, music intervention had a moderate superiority of anxiety alleviation (SMD: -0.54, 95% CI: [-0.92, -0.16]).
Discussion: Music intervention could reduce cancer-related anxiety moderately. Nevertheless, the result should be interpreted with caution as high heterogeneity in this pooled study. Well-designed trials with higher quality were still warranted in the future.
Keywords: cancer; mental health; meta-analysis; music; music therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Zang, Cheng, Zhou and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of music therapy on anxiety: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Psychiatry Res. 2021 Oct;304:114137. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2021.114137. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Psychiatry Res. 2021. PMID: 34365216 Review.
-
Efficacy of music therapy on stress and anxiety prior to dental treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 23;15:1352817. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1352817. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38463434 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of five-element music interventions in perinatal mental health and labor pain: A meta-analysis.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020 Aug;40:101217. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101217. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32763833
-
The effect of music intervention on patients with cancer-related pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Adv Nurs. 2019 Dec;75(12):3362-3373. doi: 10.1111/jan.14184. Epub 2019 Sep 16. J Adv Nurs. 2019. PMID: 31452232
-
Non-pharmacological interventions for anxiety in burn patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2020 Mar;49:102341. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102341. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Complement Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32147030
Cited by
-
Interventions to Reduce Psychosocial Burden in Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Narrative Review.J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Jan-Dec;53:19160216241251701. doi: 10.1177/19160216241251701. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 39276012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Music-Assisted Progressive Muscle Relaxation in Patients with Locally Advanced Gastric Cancer Undergoing Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy.Noise Health. 2025 May-Jun 01;27(126):210-216. doi: 10.4103/nah.nah_186_24. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Noise Health. 2025. PMID: 40574291 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the transformative impact of traditional Chinese medicine on depression: Insights from animal models.World J Psychiatry. 2024 May 19;14(5):607-623. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i5.607. eCollection 2024 May 19. World J Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38808079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of music therapy in treating depression and anxiety disorders among people with cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2023 Feb 24;14(2):69-80. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i2.69. World J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36908676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Music from Noise-Canceling Headphones Is Beneficial against Anxiety in Male Bladder Cancer Patients Undergoing Follow-Up Cystoscopy: A Prospective Randomized Trial.Urol Int. 2024;108(5):414-420. doi: 10.1159/000539312. Epub 2024 May 10. Urol Int. 2024. PMID: 38735280 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Alam M., Roongpisuthipong W., Kim N., Goyal A., Swary J., Brindise R., et al. (2016). Utility of recorded guided imagery and relaxing music in reducing patient pain and anxiety, and surgeon anxiety, during cutaneous surgical procedures: A single-blinded randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 75 585–589. 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.02.1143 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Danhauer S., Vishnevsky T., Campbell C., McCoy T., Tooze J., Kanipe K., et al. (2010). Music for patients with hematological malignancies undergoing bone marrow biopsy: A randomized controlled study of anxiety, perceived pain, and patient satisfaction. J. Soc. Integr. Oncol. 8 140–147. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

