"Smart" drug delivery: A window to future of translational medicine
- PMID: 36688039
- PMCID: PMC9846181
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1095598
"Smart" drug delivery: A window to future of translational medicine
Abstract
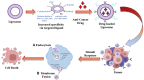
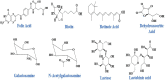
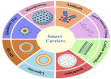
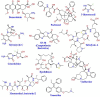
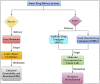
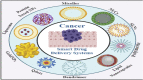
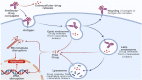
Chemotherapy is the mainstay of cancer treatment today. Chemotherapeutic drugs are non-selective and can harm both cancer and healthy cells, causing a variety of adverse effects such as lack of specificity, cytotoxicity, short half-life, poor solubility, multidrug resistance, and acquiring cancer stem-like characteristics. There is a paradigm shift in drug delivery systems (DDS) with the advent of smarter ways of targeted cancer treatment. Smart Drug Delivery Systems (SDDSs) are stimuli responsive and can be modified in chemical structure in response to light, pH, redox, magnetic fields, and enzyme degradation can be future of translational medicine. Therefore, SDDSs have the potential to be used as a viable cancer treatment alternative to traditional chemotherapy. This review focuses mostly on stimuli responsive drug delivery, inorganic nanocarriers (Carbon nanotubes, gold nanoparticles, Meso-porous silica nanoparticles, quantum dots etc.), organic nanocarriers (Dendrimers, liposomes, micelles), antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) and small molecule drug conjugates (SMDC) based SDDSs for targeted cancer therapy and strategies of targeted drug delivery systems in cancer cells.
Keywords: active targeting; cancer; nano-therapy; passive targeting; smart drug delivery systems (SDDSs); targeted cancer therapy; targeted drug delivery; translational medicine.
Copyright © 2023 Rana, Adhikary, Singh, Das and Bhatnagar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Smart nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems for cancer therapy and toxicity studies: A review.J Adv Res. 2018 Jun 25;15:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.06.005. eCollection 2019 Jan. J Adv Res. 2018. PMID: 30581608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Strategies in Stimuli-Responsive Nanocarriers as the Drug Delivery System for Enhanced Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(24):2609-2625. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190709221141. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31603055 Review.
-
Advanced targeted therapies in cancer: Drug nanocarriers, the future of chemotherapy.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Jun;93:52-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25813885 Review.
-
Smart Nanocarriers as an Emerging Platform for Cancer Therapy: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Dec 27;27(1):146. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010146. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Nanocarrier Approaches for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2021;14(3):350-366. doi: 10.2174/1874467213666200730114943. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32744982 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug Repurposing: A Conduit to Unravelling Metabolic Reprogramming for Cancer Treatment.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(8):601-627. doi: 10.2174/0113895575339660250106093738. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39835565 Review.
-
Stimulus triggered release of actives from composite microcapsules based on sporopollenin from Lycopodium clavatum.RSC Adv. 2024 Mar 28;14(15):10280-10289. doi: 10.1039/d4ra00236a. eCollection 2024 Mar 26. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38549792 Free PMC article.
-
A Modular Approach to Obtain HER2-Targeting DM1-Loaded Nanoparticles for Gastric Cancer Therapy.ACS Omega. 2024 Nov 22;9(49):48598-48606. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07442. eCollection 2024 Dec 10. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39676924 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-Based Smart Targeting and Spatial Trigger-Response Drug-Delivery Systems for Anticancer Therapy.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 15;12(1):187. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010187. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating a targeted Palbociclib-Trastuzumab loaded smart niosome platform for treating HER2 positive breast cancer cells.Int J Pharm X. 2024 Mar 11;7:100237. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100237. eCollection 2024 Jun. Int J Pharm X. 2024. PMID: 38516198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al Faraj A, Shaik, Apshaik , Asjijon (2015). Magnetic single-walled carbon nanotubes as efficient drug delivery nanocarriers in breast cancer murine model: Noninvasive monitoring using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as sensitive imaging biomarker. Int. J. Nanomedicine 10, 157–168. 10.2147/IJN.S75074 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

