Ligand and structure-based approaches for the exploration of structure-activity relationships of fusidic acid derivatives as antibacterial agents
- PMID: 36688047
- PMCID: PMC9852990
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1094841
Ligand and structure-based approaches for the exploration of structure-activity relationships of fusidic acid derivatives as antibacterial agents
Abstract
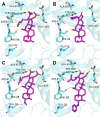
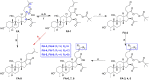
Introduction: Fusidic acid (FA) has been widely applied in the clinical prevention and treatment of bacterial infections. Nonetheless, its clinical application has been limited due to its narrow antimicrobial spectrum and some side effects. Purpose: Therefore, it is necessary to explore the structure-activity relationships of FA derivatives as antibacterial agents to develop novel ones possessing a broad antimicrobial spectrum. Methods and result: First, a pharmacophore model was established on the nineteen FA derivatives with remarkable antibacterial activities reported in previous studies. The common structural characteristics of the pharmacophore emerging from the FA derivatives were determined as those of six hydrophobic centers, two atom centers of the hydrogen bond acceptor, and a negative electron center around the C-21 field. Then, seven FA derivatives have been designed according to the reported structure-activity relationships and the pharmacophore characteristics. The designed FA derivatives were mapped on the pharmacophore model, and the Qfit values of all FA derivatives were over 50 and FA-8 possessed the highest value of 82.66. The molecular docking studies of the partial target compounds were conducted with the elongation factor G (EF-G) of S. aureus. Furthermore, the designed FA derivatives have been prepared and their antibacterial activities were evaluated by the inhibition zone test and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) test. The derivative FA-7 with a chlorine group as the substituent group at C-25 of FA displayed the best antibacterial property with an MIC of 3.125 µM. Subsequently, 3D-QSAR was carried on all the derivatives by using the CoMSIA mode of SYBYL-X 2.0. Conclusion: Hence, a computer-aided drug design model was developed for FA, which can be further used to optimize FA derivatives as highly potent antibacterial agents.
Keywords: antibacterial; derivatives; fusidic acid; pharmacophore model; structure–activity relationships.
Copyright © 2023 Zheng, Tu, Zhang, Li, Yan, Su, Deng, Sun, Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Wong, Wu, Hong and Ang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor declared a shared affiliation with the author BZ at the time of review.
Figures



Similar articles
-
3-Amino-Substituted Analogues of Fusidic Acid as Membrane-Active Antibacterial Compounds.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Mar 7;13(3):309. doi: 10.3390/membranes13030309. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984696 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Fusidic Acid Derivatives as Two-in-One Agent with Potent Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;11(8):1026. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081026. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009895 Free PMC article.
-
Methylene blue analogues: In vitro antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations and in silico pharmacophore modelling.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Feb 1;157:105603. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105603. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33091571
-
Integration of multiscale molecular modeling approaches with the design and discovery of fusidic acid derivatives.Future Med Chem. 2019 Jun;11(12):1427-1442. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2018-0567. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Future Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31304828
-
Bioactivities and Structure-Activity Relationships of Fusidic Acid Derivatives: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 15;12:759220. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.759220. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34721042 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3-Amino-Substituted Analogues of Fusidic Acid as Membrane-Active Antibacterial Compounds.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Mar 7;13(3):309. doi: 10.3390/membranes13030309. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36984696 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of chloro-methyl 2-[2-(2,6-di-chloro-phenyl-amino)-phen-yl]acetate.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2025 May 13;81(Pt 6):510-515. doi: 10.1107/S2056989025004074. eCollection 2025 Jun 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2025. PMID: 40487693 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

