Strategies of vascularization of the ethmoid labyrinth in selected even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla) and carnivores (Carnivora)
- PMID: 36688531
- PMCID: PMC10184540
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13829
Strategies of vascularization of the ethmoid labyrinth in selected even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla) and carnivores (Carnivora)
Abstract
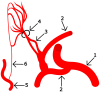
The anatomy of the nasal cavity and its structures, as well as other elements building a scaffold for olfactory organs, differs significantly among various groups of mammals. Understanding anatomical conditions of quality of olfaction are being studied worldwide and is a complex problem. Among many studies regarding bone and epithelial structures of turbinates and connected anatomical structures, few studies describe the vascularization of turbinates. Ethmoid turbinates are above all covered in olfactory epithelium containing branched axons that receive olfactory stimuli and as olfactory nerves penetrate the cribriform lamina of the ethmoid bone conveying information from smell receptors to the brain. Differences in vascularization of the cribriform plate and turbinates may add crucial information complementing studies regarding the olfactory organ's bone and soft tissue structures. In the study, we describe the vascularization of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone of 54 Artiodactyla and Carnivora.
Keywords: Carnivora; Ungulata; anatomy; angiology; cribriform plate; ethmoid artery.
© 2023 Anatomical Society.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A radiological anatomic study of the cribriform plate compared with constant structures.Rhinology. 2004 Dec;42(4):225-9. Rhinology. 2004. PMID: 15626256
-
Quantifying the cribriform plate: influences of allometry, function, and phylogeny in Carnivora.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014 Nov;297(11):2080-92. doi: 10.1002/ar.23032. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 25312366
-
The ethmoid and presphenoid of cetaceans.J Morphol. 2016 Dec;277(12):1661-1674. doi: 10.1002/jmor.20615. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Morphol. 2016. PMID: 27645469
-
Extraoral anatomy in CBCT – a literature review. Part 1: Nasoethmoidal region.Swiss Dent J. 2019 Oct 14;129(10):804-815. doi: 10.61872/sdj-2019-10-01. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Swiss Dent J. 2019. PMID: 31392880 Review.
-
Review of olfactory cleft roof anatomy.Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2023 Nov;140(6):289-295. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2023.10.011. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 2023. PMID: 37926654 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebral Vascularization and the Remaining Area Supply of the Internal Carotid Artery Derivatives of the Red Kangaroo (Osphranter rufus).Animals (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;13(17):2744. doi: 10.3390/ani13172744. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37685008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, D.R. (1972) Olfactory and non‐olfactory epithelia in the nasal cavity of the mouse, Peromyscus. American Journal of Anatomy, 133(1), 37–49. - PubMed
-
- Alsafy, M.A.M. , El‐gendy, S.A.A. & Abumandour, M.M.A. (2014) Computed tomography and Gross anatomical studies on the head of one‐humped camel (Camelus dromedarius). Anatomical Record, 297(4), 630–642. - PubMed
-
- Araujo, A.C.P. & Campos, R. (2005) A systematic study of the brain base arteries and their blood supply sources in the chinchilla (Chinchilla lanigera Molina, 1782). Brazilian Journal of Morphological Sciences, 22, 221–232.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

