Generation and Culturing of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Patient-Derived Organoids
- PMID: 36688549
- PMCID: PMC10881225
- DOI: 10.3791/64878
Generation and Culturing of High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Patient-Derived Organoids
Abstract
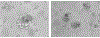
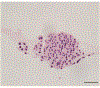
Organoids are 3D dynamic tumor models that can be grown successfully from patient-derived ovarian tumor tissue, ascites, or pleural fluid and aid in the discovery of novel therapeutics and predictive biomarkers for ovarian cancer. These models recapitulate clonal heterogeneity, the tumor microenvironment, and cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. Additionally, they have been shown to match the primary tumor morphologically, cytologically, immunohistochemically, and genetically. Thus, organoids facilitate research on tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment and are superior to cell lines. The present protocol describes distinct methods to generate patient-derived ovarian cancer organoids from patient tumors, ascites, and pleural fluid samples with a higher than 97% success rate. The patient samples are separated into cellular suspensions by both mechanical and enzymatic digestion. The cells are then plated utilizing a basement membrane extract (BME) and are supported with optimized growth media containing supplements specific to the culturing of high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC). After forming initial organoids, the PDOs can sustain long-term culture, including passaging for expansion for subsequent experiments.
Figures


References
-
- Bray F et al., Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 68 (6), 394–424 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Drost J, Clevers H Organoids in cancer research. Nature Reviews Cancer 18 (7), 407–418 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
