Systematic Comparison and Rational Design of Theophylline Riboswitches for Effective Gene Repression
- PMID: 36688639
- PMCID: PMC9927458
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02752-22
Systematic Comparison and Rational Design of Theophylline Riboswitches for Effective Gene Repression
Abstract
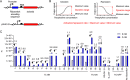
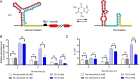
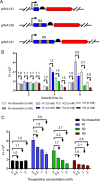
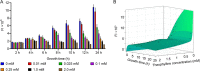
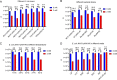
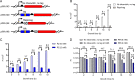
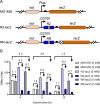
Riboswitches are promising regulatory tools in synthetic biology. To date, 25 theophylline riboswitches have been developed for regulation of gene expression in bacteria. However, no one has systematically evaluated their regulatory effects. To promote efficient selection and application of theophylline riboswitches, we examined 25 theophylline riboswitches in Escherichia coli MG1655 and found that they varied widely in terms of activation/repression ratios and expression levels in the absence of theophylline. Of the 20 riboswitches that activate gene expression, only one exhibited a high activation ratio (63.6-fold) and low expression level without theophylline. Furthermore, none of the five riboswitches that repress gene expression were more than 2.0-fold efficient. To obtain an effective repression system, we rationally designed a novel theophylline riboswitch to control a downstream gene or genes by premature transcription termination. This riboswitch allowed theophylline-dependent downregulation of the TurboRFP reporter in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Its performance profile exceeded those of previously described repressive theophylline riboswitches. We then introduced as the second part a RepA tag (protein degradation tag) coding sequence fused at the 5'-terminal end of the turborfp gene, which further reduced protein level, while not reducing the repressive effect of the riboswitch. By combining two tandem theophylline riboswitches with a RepA tag, we constructed a regulatory cassette that represses the expression of the gene(s) of interest at both the transcriptional and posttranslational levels. This regulatory cassette can be used to repress the expression of any gene of interest and represents a crucial step toward harnessing theophylline riboswitches and expanding the synthetic biology toolbox. IMPORTANCE A variety of gene expression regulation tools with significant regulatory effects are essential for the construction of complex gene circuits in synthetic biology. Riboswitches have received wide attention due to their unique biochemical, structural, and genetic properties. Here, we have not only systematically and precisely characterized the regulatory properties of previously developed theophylline riboswitches but also engineered a novel repressive theophylline riboswitch acting at the transcriptional level. By introducing coding sequences of a tandem riboswitch and a RepA protein degradation tag at the 5' end of the reporter gene, we successfully constructed a simple and effective regulatory cassette for gene regulation. Our work provides useful biological components for the construction of synthetic biology gene circuits.
Keywords: biological parts; posttranslational regulation; protein degradation tag; theophylline riboswitch; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Creation of Architecturally Minimal Transcriptionally Activating Riboswitches Responsive to Theophylline Reveals an Unconventional Design Strategy.ACS Synth Biol. 2023 Dec 15;12(12):3716-3729. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.3c00519. Epub 2023 Dec 5. ACS Synth Biol. 2023. PMID: 38052004
-
Design criteria for synthetic riboswitches acting on transcription.RNA Biol. 2015;12(2):221-31. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017235. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25826571 Free PMC article.
-
A Theophylline-Responsive Riboswitch Regulates Expression of Nuclear-Encoded Genes.Plant Physiol. 2020 Jan;182(1):123-135. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00625. Epub 2019 Nov 8. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31704721 Free PMC article.
-
Riboswitches: discovery of drugs that target bacterial gene-regulatory RNAs.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Dec 20;44(12):1329-38. doi: 10.1021/ar200039b. Epub 2011 May 26. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21615107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-Transcriptional Folding and Regulation Mechanisms of Riboswitches.Molecules. 2017 Jul 13;22(7):1169. doi: 10.3390/molecules22071169. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28703767 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of the dual regulation by a c-di-GMP riboswitch Bc1 with a long expression platform from Bacillus thuringiensis.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0045024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00450-24. Epub 2024 May 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38819160 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential riboswitch elements in Homo sapiens mRNA 5'UTR sequences using positive-unlabeled machine learning.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 24;20(4):e0320282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320282. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40273288 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic search for RNA structural switches across the human transcriptome.Nat Methods. 2024 Sep;21(9):1634-1645. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02335-1. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Nat Methods. 2024. PMID: 39014073 Free PMC article.
-
A Multi-Layer-Controlled Strategy for Cloning and Expression of Toxin Genes in Escherichia coli.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 18;15(8):508. doi: 10.3390/toxins15080508. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37624265 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential riboswitch elements inHomo SapiensmRNA 5'UTR sequences using Positive-Unlabeled machine learning.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 6:2023.11.23.568398. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.23.568398. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS One. 2025 Apr 24;20(4):e0320282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320282. PMID: 39677788 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

