The influence of receptor expression and clinical subtypes on baseline [18F]FDG uptake in breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36689007
- PMCID: PMC9871105
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-023-00953-y
The influence of receptor expression and clinical subtypes on baseline [18F]FDG uptake in breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: To quantify the relationship between [18F]FDG uptake of the primary tumour measured by PET-imaging with immunohistochemical (IHC) expression of ER, PR, HER2, Ki-67, and clinical subtypes based on these markers in breast cancer patients.
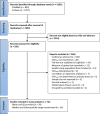
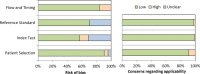
Methods: PubMed and Embase were searched for studies that compared SUVmax between breast cancer patients negative and positive for IHC expression of ER, PR, HER2, Ki-67, and clinical subtypes based on these markers. Two reviewers independently screened the studies and extracted the data. Standardized mean differences (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated by using DerSimonian-Laird random-effects models. P values less than or equal to 5% indicated statistically significant results.
Results: Fifty studies were included in the final analysis. SUVmax is significantly higher in ER-negative (31 studies, SMD 0.66, 0.56-0.77, P < 0.0001), PR-negative (30 studies, SMD 0.56; 0.40-0.71, P < 0.0001), HER2-positive (32 studies, SMD - 0.29, - 0.49 to - 0.10, P = 0.0043) or Ki-67-positive (19 studies, SMD - 0.77; - 0.93 to - 0.61, P < 0.0001) primary tumours compared to their counterparts. The majority of clinical subtypes were either luminal A (LA), luminal B (LB), HER2-positive or triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). LA is associated with significantly lower SUVmax compared to LB (11 studies, SMD - 0.49, - 0.68 to - 0.31, P = 0.0001), HER2-positive (15 studies, SMD - 0.91, - 1.21 to - 0.61, P < 0.0001) and TNBC (17 studies, SMD - 1.21, - 1.57 to - 0.85, P < 0.0001); and LB showed significantly lower uptake compared to TNBC (10 studies, SMD - 0.77, - 1.05 to - 0.49, P = 0.0002). Differences in SUVmax between LB and HER2-positive (9 studies, SMD - 0.32, - 0.88 to 0.24, P = 0.2244), and HER2-positive and TNBC (17 studies, SMD - 0.29, - 0.61 to 0.02, P = 0.0667) are not significant.
Conclusion: Primary tumour SUVmax is significantly higher in ER-negative, PR-negative, HER2-positive and Ki-67-positive breast cancer patients. Luminal tumours have the lowest and TNBC tumours the highest SUVmax. HER2 overexpression has an intermediate effect.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Clinical subtypes; Immunohistochemistry; Meta-analyses; Systematic review; [18F]FDG PET.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined 18F-FDG and 18F-Alfatide II PET May Predict Luminal B (HER2 Negative) Subtype and Nonluminal Subtype of Invasive Breast Cancer.Mol Pharm. 2022 Sep 5;19(9):3405-3411. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00547. Epub 2022 Aug 16. Mol Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35972444
-
18F-FDG uptake in breast cancer correlates with immunohistochemically defined subtypes.Eur Radiol. 2014 Mar;24(3):610-8. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-3037-1. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Eur Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24097303
-
Correlation of breast cancer subtypes, based on estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2, with functional imaging parameters from ⁶⁸Ga-RGD PET/CT and ¹⁸F-FDG PET/CT.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014 Aug;41(8):1534-43. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2744-4. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24652232
-
Comparison of triple-negative and estrogen receptor-positive/progesterone receptor-positive/HER2-negative breast carcinoma using quantitative fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose/positron emission tomography imaging parameters: a potentially useful method for disease characterization.Cancer. 2008 Mar 1;112(5):995-1000. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23226. Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18098228 Clinical Trial.
-
Intercontinental Comparison of Immunohistochemical Subtypes Among Individuals With Breast Cancer in South-East Asia and South America: A Scoping Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies.World J Oncol. 2024 Jun;15(3):355-371. doi: 10.14740/wjon1788. Epub 2024 May 7. World J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38751698 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Novel Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer with PET Imaging.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 21;60(12):2099. doi: 10.3390/medicina60122099. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Imaging Parameters of 18F FDG PET/CT in Differentiating the Ki-67 Index in Carcinoma Breast.Indian J Nucl Med. 2025 Mar-Apr;40(2):67-71. doi: 10.4103/ijnm.ijnm_168_24. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Indian J Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40735764 Free PMC article.
-
An Innovative Non-Linear Prediction Model for Clinical Benefit in Women with Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Using Baseline FDG-PET/CT and Clinical Data.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 20;15(22):5476. doi: 10.3390/cancers15225476. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001736 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and economic outcomes of adding [18F]FES PET/CT in estrogen receptor status identification in metastatic and recurrent breast cancer in the US.PLoS One. 2024 May 14;19(5):e0302486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302486. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38743917 Free PMC article.
-
18F-FDG PET-Derived Volume-Based Parameters to Predict Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Grade III Breast Cancer of Different Molecular Subtypes Candidates to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 11;15(10):2715. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102715. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, Harvey BE, Mangu PB, Bartlett JMS, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(20):2105–2122. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.8738. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous