Repeated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: induction of high-avidity anti-RBD neutralizing antibodies
- PMID: 36689013
- PMCID: PMC9869844
- DOI: 10.1007/s10147-023-02295-0
Repeated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: induction of high-avidity anti-RBD neutralizing antibodies
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Repeated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: induction of high-avidity anti-RBD neutralizing antibodies.Int J Clin Oncol. 2023 Mar;28(3):370. doi: 10.1007/s10147-023-02310-4. Int J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36805385 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
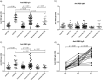
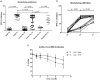
Background: Cancer patients are more vulnerable to COVID-19 and are thus given high priority in vaccination campaigns. In solid cancer patients treated with checkpoint inhibitors, we evaluated the amount of anti-RBD and neutralizing antibodies and antibody avidity after two or three doses of the vaccine.
Methods: Thirty-eight solid cancer patients, 15 untreated hematological patients and 21 healthy subjects were enrolled in the study. Blood was collected before the first dose (T0), 21 days after the second (T2) and in 18 solid cancer patients also 15 days after the third dose of vaccine (T3). IgG, IgM and IgA anti-RBD antibodies were detected by ELISA. Neutralizing antibodies were measured testing the inhibition of RBD binding to ACE2. Antibody avidity was evaluated in 18 patients by a urea avidity ELISA.
Results: IgG anti-RBD antibodies were produced in 65.8% of the cancer patients at T2, and in 60% of hematological patients at levels lower than healthy controls. IgM and IgA anti-RBD antibodies were also produced in 5.3% and 21% cancer patients, respectively. At T3, a significant increase in anti-RBD IgG levels was observed. Neutralizing antibodies were produced in 68.4% of cancer patients as compared with 93% of untreated hematological patients and 100% of controls, at titers lower than in healthy subjects. At T3, neutralizing antibodies and avidity of IgG anti-RBD increased; 6/18 patients negative at T2 developed neutralizing antibodies at T3.
Conclusion: The data indicate that in cancer patients mRNA vaccine induces high avidity anti-RBD antibodies and neutralizing antibodies that increase after the third dose. The process of induction and selection of high-affinity antibodies is apparently unaffected by the treatment with anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies.
Keywords: Anti-Spike antibodies; Antibody avidity; Immune Checkpoint inhibitors; MRNA vaccine; Neutralizing antibodies; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibody Avidity and Neutralizing Response against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant after Infection or Vaccination.J Immunol Res. 2022 Aug 31;2022:4813199. doi: 10.1155/2022/4813199. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36093434 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of neutralizing antibodies in CLL patients after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination: a monocentric experience.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Aug;23(4):1197-1203. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00877-2. Epub 2022 Sep 8. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36074205 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of SARS-CoV-2 Viral Neutralizing Antibody Titers with Anti-Spike Antibodies and ACE-2 Inhibition among Vaccinated Individuals.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0131522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01315-22. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36121252 Free PMC article.
-
Are SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Detectable in Human Milk After Vaccination Against COVID-19?J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022 Apr 30;11(4):126. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piac024. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2022. PMID: 35394545 Free PMC article.
-
Response and Duration of Serum Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies After Inactivated Vaccination Within 160 Days.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 23;12:786554. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.786554. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003104 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

