Solanum nigrum L. in COVID-19 and post-COVID complications: a propitious candidate
- PMID: 36689040
- PMCID: PMC9868520
- DOI: 10.1007/s11010-022-04654-3
Solanum nigrum L. in COVID-19 and post-COVID complications: a propitious candidate
Abstract
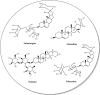
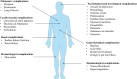
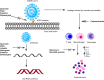
COVID-19 is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, SARS-CoV-2. COVID-19 has changed the world scenario and caused mortality around the globe. Patients who recovered from COVID-19 have shown neurological, psychological, renal, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and hematological complications. In some patients, complications lasted more than 6 months. However, significantly less attention has been given to post-COVID complications. Currently available drugs are used to tackle the complications, but new interventions must address the problem. Phytochemicals from natural sources have been evaluated in recent times to cure or alleviate COVID-19 symptoms. An edible plant, Solanum nigrum, could be therapeutic in treating COVID-19 as the AYUSH ministry of India prescribes it during the pandemic. S. nigrum demonstrates anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antiviral action to treat the SARS-CoV-2 infection and its post-complications. Different parts of the plant represent a reduction in proinflammatory cytokines and prevent multi-organ failure by protecting various organs (liver, kidney, heart, neuro, and lung). The review proposes the possible role of the plant S. nigrum in managing the symptoms of COVID-19 and its post-COVID complications based on in silico docking and pharmacological studies. Further systematic and experimental studies are required to validate our hypothesis.
Keywords: COVID-19; Post-COVID complications; SARS-CoV-2 Phytochemicals; Solanum nigrum.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In silico study on spice-derived antiviral phytochemicals against SARS-CoV-2 TMPRSS2 target.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(22):11874-11884. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2021.1965658. Epub 2021 Aug 24. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 34427179
-
Cyclosporine A Inhibits Viral Infection and Release as Well as Cytokine Production in Lung Cells by Three SARS-CoV-2 Variants.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0150421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01504-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 34985303 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis-directed therapy of 2019 novel coronavirus disease.J Med Virol. 2021 Mar;93(3):1320-1342. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26610. Epub 2020 Nov 10. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33073355 Review.
-
Putative mechanism of neurological damage in COVID-19 infection.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2021;81(1):69-79. doi: 10.21307/ane-2021-008. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2021. PMID: 33949163 Review.
-
Antiviral effects of phytochemicals against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and their mechanisms of action: A review.Phytother Res. 2023 Mar;37(3):1036-1056. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7671. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Phytother Res. 2023. PMID: 36343627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Solamargine acts as an antiviral by interacting to MZF1 and targeting the core promoter of the hepatitis B virus gene.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Aug 10;16(15):11668-11682. doi: 10.18632/aging.206047. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39133152 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the apoptosis of human melanoma cells induced by solanine in vitro and its mechanisms.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Dec 30;317(1):163. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03665-y. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39738917
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

