Towards accurate 177Lu SPECT activity quantification and standardization using lesion-to-background voxel ratio
- PMID: 36689080
- PMCID: PMC9871126
- DOI: 10.1186/s40658-023-00526-x
Towards accurate 177Lu SPECT activity quantification and standardization using lesion-to-background voxel ratio
Abstract
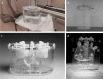
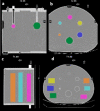
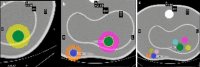
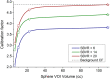
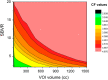
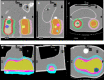
Background: Conventional calibration of the gamma camera consists of the calculation of calibration factors (CFs) (ratio of counts/cc and true concentration activity) as the function of the volume of interest (VOI). However, such method shows inconsistent results when the background activity varies. The aim of the present study was to propose a new calibration method by considering the sphere-to-background counts/voxel ratio (SBVR) in addition to the VOI for CFs calculation. A PET cylindrical flood phantom, a NEMA IQ body phantom, a Data spectrum Torso Phantom (ECT/TOR/P) and a LK-S Kyoto Liver/Kidney phantom were used. The NEMA IQ phantom was used to calibrate the camera and to produce CFs for the different spheres volumes and for varying sphere-to-background activity ratios. The spheres were filled with a uniform activity concentration of 177Lu, while the background was first filled with cold water and activity was added between each SPECT scan. SPECT imaging was performed for 30-s, 20-s, and 10-s exposure per view. The calculated CFs were expressed as function of the sphere volume and SBVR. The obtained CFs were validated for an additional NEMA IQ acquisition with different activities in spheres and background and for the Torso and Liver/Kidney phantoms with inserted NEMA IQ spheres. The quantification accuracy was compared with the conventional method not taking SBVR into consideration.
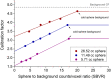
Results: The relative errors in quantification using the NEMA IQ phantom with the new calibration method were 0.16%, 5.77%, 9.34% for the large, medium and small sphere, respectively, for a time per view of 30-s. The conventional calibration method gave errors of 3.65%, 6.65%, 30.28% for 30-s. The LK-S Kyoto Liver/Kidney Phantom resulted in quantification errors of 3.40%, 2.14%, 11.18% for the large, medium and small spheres, respectively, for 30-s; compared to 11.31%, 17.54%, 14.43% for 30-s, respectively, for the conventional method. Similar results were obtained for shorter acquisitions times with 20-s and 10-s time per view.
Conclusion: These results suggest that SBVR allows to improve quantification accuracy. The shorter time-per-view acquisitions had similar relative differences compared to the full-time acquisition which allows shorter imaging times with 177Lu and improved patient comfort. The SBVR method is simple to set up and can be proposed for standardization.
Keywords: 177Lu activity quantification; Calibration factors; Gamma camera calibration; SPECT; Sphere-to-background counts/voxel ratio.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of calibration factors and recovery coefficients on 177Lu SPECT activity quantification accuracy: a Monte Carlo study.EJNMMI Phys. 2021 Mar 18;8(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s40658-021-00365-8. EJNMMI Phys. 2021. PMID: 33738605 Free PMC article.
-
A multicentre and multi-national evaluation of the accuracy of quantitative Lu-177 SPECT/CT imaging performed within the MRTDosimetry project.EJNMMI Phys. 2021 Jul 23;8(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s40658-021-00397-0. EJNMMI Phys. 2021. PMID: 34297218 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative accuracy of 177Lu SPECT imaging for molecular radiotherapy.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 14;12(8):e0182888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182888. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28806773 Free PMC article.
-
Position dependence of recovery coefficients in 177Lu-SPECT/CT reconstructions - phantom simulations and measurements.EJNMMI Phys. 2024 Jun 28;11(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s40658-024-00662-y. EJNMMI Phys. 2024. PMID: 38937408 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of 177Lu activity quantification using MCNP5-Modeled SPECT imaging.Appl Radiat Isot. 2025 Jun;220:111786. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2025.111786. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Appl Radiat Isot. 2025. PMID: 40121923
Cited by
-
Tumor dosimetry using 177Lu: influence of background activity, measurement method and reconstruction algorithm.EJNMMI Phys. 2023 Jun 21;10(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s40658-023-00561-8. EJNMMI Phys. 2023. PMID: 37341930 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Evaluation of a Portable Pinhole SPECT System for 177Lu Imaging: Monte Carlo Simulations and Experimental Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 30;15(11):1387. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15111387. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40506959 Free PMC article.
-
Activity quantification and dosimetry in radiopharmaceutical therapy with reference to 177Lutetium.Front Nucl Med. 2024 Mar 28;4:1355912. doi: 10.3389/fnume.2024.1355912. eCollection 2024. Front Nucl Med. 2024. PMID: 39355215 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kondev FG. Nuclear data sheets for A = 177. Nucl Data Sheets. 2003;98:801–1095. doi: 10.1006/ndsh.2003.0006. - DOI
-
- Chicheportiche A, Ben-Haim S, Grozinsky-Glasberg S, Oleinikov K, Meirovitz A, Gross DJ, et al. Dosimetry after peptide receptor radionuclide therapy: impact of reduced number of post-treatment studies on absorbed dose calculation and on patient management. EJNMMI Phys. 2020;7:5. doi: 10.1186/s40658-020-0273-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

