Structure-Directed Discovery of Potent Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 36689364
- PMCID: PMC9974930
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01996
Structure-Directed Discovery of Potent Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
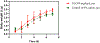
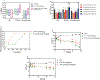
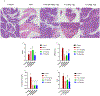
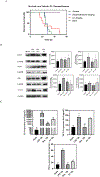
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) has been identified as an attractive target for anti-inflammatory drug design in recent years. Picomolar level compound G1 against sEH was obtained by introducing the hydrophilic group homopiperazine and hydrophobic fragment propionyl onto the structure of lead compound A. G1 showed good microsomal stability, a moderate plasma protein binding rate, and good oral bioavailability and was well tolerated in rats. G1 has significant analgesic effects on CFA-induced AIA mice, ameliorated the pancreatic injury in acute pancreatitis induced by l-arginine, reversed pancreatic injury, edema, and neutrophil infiltration, and increased the survival time of C57BL/6 mice in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced sepsis model. Moreover the expression levels of sEH, COX-2, NOS-2, vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM), IL-6, MCP-5, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) were measured by Western blot or enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), with varying degrees of decrease. These results suggested that G1 is a drug candidate worthy of further evaluation for the treatment of inflammation-induced diseases such as arthritis, acute pancreatitis, and sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interes
Figures








Similar articles
-
Screening of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory ingredients from traditional Chinese medicines for anti-inflammatory use.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Dec 24;194:475-482. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.044. Epub 2016 Oct 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27702689 Free PMC article.
-
From the Design to the In Vivo Evaluation of Benzohomoadamantane-Derived Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis.J Med Chem. 2021 May 13;64(9):5429-5446. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01601. Epub 2021 May 4. J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33945278 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury and Improves Survival in Mice.Shock. 2017 May;47(5):638-645. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000767. Shock. 2017. PMID: 27753791 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecule Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitors in Multitarget and Combination Therapies for Inflammation and Cancer.Molecules. 2020 Nov 24;25(23):5488. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235488. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33255197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting soluble epoxide hydrolase for inflammation and pain - an overview of pharmacology and the inhibitors.Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2012 Apr;11(2):143-58. doi: 10.2174/187152812800392823. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 22280237 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Synthesis of Dual-Targeting Inhibitors of sEH and HDAC6 for the Treatment of Neuropathic Pain and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mortality.J Med Chem. 2024 Feb 8;67(3):2095-2117. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c02006. Epub 2024 Jan 18. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38236416 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of selective ROCK2 inhibitors with free radical scavenging ability for the treatment of gouty arthritis.Mol Divers. 2025 Jan 23. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-11054-w. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 39847187
References
-
- Xiao AY; Tan ML; Wu LM; Asrani VM; Windsor JA; Yadav D; Petrov MS Global incidence and mortality of pancreatic diseases: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of population-based cohort studies. Lancer. Gastroenterol 2016, 1, 45–55. - PubMed
-
- Mei F; Yu J; Li M; Xiang M; Hong Y; Zhou Y; You Y; Xia H; Jin H; Wang W Magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate alleviates liver injury in obese rats with acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Pathol. Res Pract 2019, 215, 106–114. - PubMed
-
- Forsmark CE; Vege SS; Wilcox CM Acute pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med 2016, 375, 1972–1981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

