Small-Molecule Polθ Inhibitors Provide Safe and Effective Tumor Radiosensitization in Preclinical Models
- PMID: 36689546
- PMCID: PMC10102842
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2977
Small-Molecule Polθ Inhibitors Provide Safe and Effective Tumor Radiosensitization in Preclinical Models
Abstract
Purpose: DNA polymerase theta (Polθ, encoded by the POLQ gene) is a DNA repair enzyme critical for microhomology mediated end joining (MMEJ). Polθ has limited expression in normal tissues but is frequently overexpressed in cancer cells and, therefore, represents an ideal target for tumor-specific radiosensitization. In this study we evaluate whether targeting Polθ with novel small-molecule inhibitors is a feasible strategy to improve the efficacy of radiotherapy.
Experimental design: We characterized the response to Polθ inhibition in combination with ionizing radiation in different cancer cell models in vitro and in vivo.
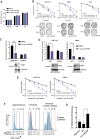
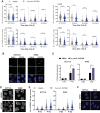
Results: Here, we show that ART558 and ART899, two novel and specific allosteric inhibitors of the Polθ DNA polymerase domain, potently radiosensitize tumor cells, particularly when combined with fractionated radiation. Importantly, noncancerous cells were not radiosensitized by Polθ inhibition. Mechanistically, we show that the radiosensitization caused by Polθ inhibition is most effective in replicating cells and is due to impaired DNA damage repair. We also show that radiosensitization is still effective under hypoxia, suggesting that these inhibitors may help overcome hypoxia-induced radioresistance. In addition, we describe for the first time ART899 and characterize it as a potent and specific Polθ inhibitor with improved metabolic stability. In vivo, the combination of Polθ inhibition using ART899 with fractionated radiation is well tolerated and results in a significant reduction in tumor growth compared with radiation alone.
Conclusions: These results pave the way for future clinical trials of Polθ inhibitors in combination with radiotherapy.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures



References
-
- Wilkinson E. New technical guidance to boost global radiotherapy access. Lancet Oncol 2021;22:589–90. - PubMed
-
- Hanna TP, Shafiq J, Delaney GP, Vinod SK, Thompson SR, Barton MB. The population benefit of evidence-based radiotherapy: 5-year local control and overall survival benefits. Radiother Oncol 2018;126:191–7. - PubMed
-
- Higgins GS, O'Cathail SM, Muschel RJ, McKenna WG. Drug radiotherapy combinations: review of previous failures and reasons for future optimism. Cancer Treat Rev 2015;41:105–13. - PubMed
-
- Kawamura K, Bahar R, Seimiya M, Chiyo M, Wada A, Okada S, et al. . DNA polymerase theta is preferentially expressed in lymphoid tissues and upregulated in human cancers. Int J Cancer 2004;109:9–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

