[Thyrotoxicosis in a patient with Turner syndrome: radioactive iodine therapy]
- PMID: 36689711
- PMCID: PMC9939966
- DOI: 10.14341/probl13132
[Thyrotoxicosis in a patient with Turner syndrome: radioactive iodine therapy]
Abstract
Turner syndrome (TS) is a chromosomal disorder affecting female and characterized by complete or partial monosomy of the X chromosome. These genetic changes lead to the abnormalities in growth and development and increase the risk of autoimmune diseases, including those affecting the thyroid. Thyroid pathology in TS may include autoimmune thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis (Graves disease, AIT in the hyperthyroid state).Thyrotoxicosis is the clinical syndrome of excess circulating thyroid hormones. One of the main causes of thyrotoxicosis is Graves' disease (GD), an organ-specific autoimmune disease caused by the production of stimulating thyrotropin receptor antibodies. There are three treatment options for thyrotoxicosis: anti-thyroid drugs, radioactive iodine and thyroidectomy. A personalized approach to disease management is especially important in cases of genetic diseases.We present a clinical case of a patient with TS and GD, who has been referred to a radiologist at the Department of Radionuclide Therapy of Endocrinology Research Center. The patient was diagnosed with congenital hypothyroidism at neonatal screening, but thyroid hormones therapy was initiated aged three. Based on the survey, GD was diagnosed aged twenty one. Anti-thyroid drug therapy was started, which resulted in toxic hepatitis. Taking into account intolerance to anti-thyroid drugs, radioiodine therapy has been recommended, which led to hypothyroidism.
Синдромом Шерешевского–Тернера (СШТ) - хромосомное заболевание, при котором в клетках женского организма одна Х-хромосома нормальная, а другая отсутствует или структурно изменена. Данные генетические аберрации приводят к появлению ряда отклонений в росте и развитии и повышают риск развития аутоиммунных заболеваний, в том числе затрагивающих щитовидную железу (ЩЖ). Патология ЩЖ при СШТ может быть представлена аутоиммунным тиреоидитом (АИТ), гипотиреозом или тиреотоксикозом различного генеза (болезнь Грейвса (БГ), АИТ в стадии тиреотоксикоза).Тиреотоксикоз — синдром, обусловленный избытком циркулирующих в крови гормонов ЩЖ. Одна из основных причин тиреотоксикоза — БГ, органоспецифичное аутоиммунное заболевание, обусловленное выработкой стимулирующих антител к рецепторам тиреотропного гормона. Существует три варианта лечения тиреотоксикоза при БГ: консервативный, хирургический, радионуклидный. Персонализированный подход к лечению особенно важен при наличии у пациента сопутствующих фоновых заболеваний, затрагивающих генотип.Мы представляем клинический случай пациентки Б. с СШТ и БГ, которая направлена к радиологу в отделение радионуклидной терапии ФГБУ «НМИЦ эндокринологии» Минздрава России. Особенности анамнеза: на этапе неонатального скрининга у пациентки диагностирован врожденный гипотиреоз, в возрасте 3 лет инициирована терапия тиреоидными гормонами. В возрасте 21 года у пациентки манифестировал тиреотоксикоз, причиной которого была БГ. На фоне тиреостатической терапии развился токсический гепатит. С учетом непереносимости консервативной терапии рекомендована терапия радиоактивным йодом 131I, в результате которой развился гипотиреоз.
Figures
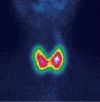
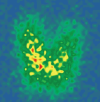
Similar articles
-
Hyperthyroidism: A Review.JAMA. 2023 Oct 17;330(15):1472-1483. doi: 10.1001/jama.2023.19052. JAMA. 2023. PMID: 37847271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyrotoxicosis - investigation and management .Clin Med (Lond). 2017 Jun;17(3):274-277. doi: 10.7861/clinmedicine.17-3-274. Clin Med (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28572231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Follow-Up of Thyroid Function in Children With Neonatal Hyperthyroidism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 4;13:877119. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.877119. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35600602 Free PMC article.
-
Thyrotoxicosis.Dis Mon. 1997 Sep;43(9):601-77. Dis Mon. 1997. PMID: 9301645 Review.
-
[Autoimmune diseases of the thyroid gland].Internist (Berl). 2017 Jan;58(1):47-58. doi: 10.1007/s00108-016-0171-2. Internist (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28074218 Review. German.
References
-
- Volevodz N.N. Federal'nye klinicheskie rekomendatsii «Cindrom Shereshevskogo–Ternera (SShT): klinika, diagnostika, lechenie» // Problemy Endokrinologii. — 2014. — T. 60. — №April. — S. 65-76.
-
- Wegiel Malgorzata, Antosz Aleksandra, Gieburowska Joanna, Szeliga Kamila, Hankus Magdalena, Grzybowska-Chlebowczyk Urszula, Wiecek Sabina, Malecka-Tendera Ewa, Gawlik Aneta. Autoimmunity Predisposition in Girls With Turner Syndrome. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2019 Jul;10 doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00511. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
