Genomic glucocorticoid action in embryonic mouse neural stem cells
- PMID: 36690169
- PMCID: PMC10057471
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2023.111864
Genomic glucocorticoid action in embryonic mouse neural stem cells
Abstract
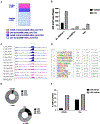
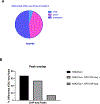
Prenatal exposure to synthetic glucocorticoids (sGCs) reprograms brain development and predisposes the developing fetus towards potential adverse neurodevelopmental outcomes. Using a mouse model of sGC administration, previous studies show that these changes are accompanied by sexually dimorphic alterations in the transcriptome of neural stem and progenitor cells (NSPCs) derived from the embryonic telencephalon. Because cell type-specific gene expression profiles tightly regulate cell fate decisions and are controlled by a flexible landscape of chromatin domains upon which transcription factors and enhancer elements act, we multiplexed data from four genome-wide assays: RNA-seq, ATAC-seq (assay for transposase accessible chromatin followed by genome wide sequencing), dual cross-linking ChIP-seq (chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by genome wide sequencing), and microarray gene expression to identify novel relationships between gene regulation, chromatin structure, and genomic glucocorticoid receptor (GR) action in NSPCs. These data reveal that GR binds preferentially to predetermined regions of accessible chromatin to influence gene programming and cell fate decisions. In addition, we identify SOX2 as a transcription factor that impacts the genomic response of select GR target genes to sGCs (i.e., dexamethasone) in NSPCs.
Keywords: Chromatin; Glucocorticoid; Neural stem progenitor; Neurodevelopment; SOX2.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest None of the authors have any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 regulates genomic action of the glucocorticoid receptor in neural stem cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;34(14):2611-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01121-13. Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24777604 Free PMC article.
-
Differential subcellular localization of the glucocorticoid receptor in distinct neural stem and progenitor populations of the mouse telencephalon in vivo.Brain Res. 2013 Jul 26;1523:10-27. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23751362 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the chromatin landscape and sequence in determining cell type-specific genomic glucocorticoid receptor binding and gene regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 28;45(4):1805-1819. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1163. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27903902 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic effects of glucocorticoids.Protoplasma. 2017 May;254(3):1175-1185. doi: 10.1007/s00709-016-1063-y. Epub 2016 Dec 24. Protoplasma. 2017. PMID: 28013411 Review.
-
Glucocorticoid Signaling: An Update from a Genomic Perspective.Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:155-80. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105323. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26667074 Review.
References
-
- ACOG committee opnion: antenatal corticosteroid therapy for fetal maturation. Obstetrics and gynecology 99, 871–873 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Liggins GC & Howie RN A controlled trial of antepartum glucocorticoid treatment for prevention of the respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants. Pediatrics 50, 515–525 (1972). - PubMed
-
- Franca MS et al. Neonatal neuronal apoptosis after betamethasone administration in pregnant Wistar rats. The journal of maternal-fetal & neonatal medicine : the official journal of the European Association of Perinatal Medicine, the Federation of Asia and Oceania Perinatal Societies, the International Society of Perinatal Obstet 29, 1089–1093, doi:10.3109/14767058.2015.1035639 (2016). - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

