Bacterial epiglottitis superimposed on oropharyngeal cancer: A case report
- PMID: 36690392
- PMCID: PMC10026303
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.1783
Bacterial epiglottitis superimposed on oropharyngeal cancer: A case report
Abstract
Background: Patients undergoing chemotherapy and radiotherapy are placed in an immunocompromised state worth consideration in the event of potential airway compromise, especially when superimposed on an airway-obstructing tumor. We report a case of bacterial epiglottitis in a patient with active oropharyngeal cancer (OPC), who presented in such a way that an infectious etiology was not initially considered in the patient's care. To our knowledge, such a circumstance has not been reported in the literature.
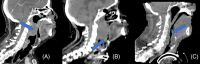
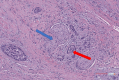
Case: Here, we report a case of a 68-year-old male with advanced-stage OPC who developed respiratory distress and underwent emergent tracheostomy. The patient was diagnosed postoperatively with Haemophilus influenza and Pseudomonas aerugeniosa. Following antibiotic treatment, the patient recovered to the point in which he could then undergo concomitant chemoradiation. The patient later had a recurrence of P. aerugeniosa during their radiotherapy that was also treated with antibiotics. The patient experienced continued symptoms related to their OPC and underwent pharyngectomy. Despite the initial success of this procedure, the patient experienced tumor recurrence and succumbed to his disease.
Conclusion: This case underscores the importance of considering multiple etiologies concerning airway compromise, as the consequence of delayed cancer treatment may be loss of local cancer control.
Keywords: airway-obstructing tumor; emergent tracheostomy; epiglottitis; oropharyngeal cancer; recurrent airway infection.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have stated explicitly that there are no conflicts of interest in connection with this article.
Figures


References
-
- Jamal Z, Anjum F. Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; 2022. - PubMed
-
- Guldfred LA, Lyhne D, Becker BC. Acute epiglottitis: epidemiology, clinical presentation, management and outcome. J Laryngol Otol. 2008;122:818‐823. - PubMed
-
- Hermansen MN, Schmidt JH, Krug AH, Larsen K, Kristensen S. Low incidence of children with acute epiglottis after introduction of vaccination. Dan Med J. 2014;61:A4788. - PubMed
-
- Shah RK, Roberson DW, Jones DT. Epiglottitis in the Hemophilus influenzae type b vaccine era: changing trends. Laryngoscope. 2004;114:557‐560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

