Screening cell-cell communication in spatial transcriptomics via collective optimal transport
- PMID: 36690742
- PMCID: PMC9911355
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-022-01728-4
Screening cell-cell communication in spatial transcriptomics via collective optimal transport
Abstract
Spatial transcriptomic technologies and spatially annotated single-cell RNA sequencing datasets provide unprecedented opportunities to dissect cell-cell communication (CCC). However, incorporation of the spatial information and complex biochemical processes required in the reconstruction of CCC remains a major challenge. Here, we present COMMOT (COMMunication analysis by Optimal Transport) to infer CCC in spatial transcriptomics, which accounts for the competition between different ligand and receptor species as well as spatial distances between cells. A collective optimal transport method is developed to handle complex molecular interactions and spatial constraints. Furthermore, we introduce downstream analysis tools to infer spatial signaling directionality and genes regulated by signaling using machine learning models. We apply COMMOT to simulation data and eight spatial datasets acquired with five different technologies to show its effectiveness and robustness in identifying spatial CCC in data with varying spatial resolutions and gene coverages. Finally, COMMOT identifies new CCCs during skin morphogenesis in a case study of human epidermal development.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

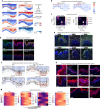

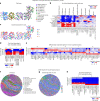
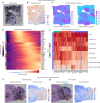




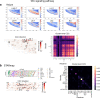

Comment in
-
A mathematical method and software for spatially mapping intercellular communication.Nat Methods. 2023 Feb;20(2):185-186. doi: 10.1038/s41592-022-01729-3. Nat Methods. 2023. PMID: 36693905 No abstract available.
References
-
- Svensson V, Vento-Tormo R, Teichmann SA. Exponential scaling of single-cell RNA-seq in the past decade. Nat. Protoc. 2018;13:599–604. - PubMed
-
- Efremova M, Vento-Tormo M, Teichmann SA, Vento-Tormo R. CellPhoneDB: inferring cell–cell communication from combined expression of multi-subunit ligand–receptor complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2020;15:1484–1506. - PubMed

