Potent Dual Polymerase/Exonuclease Inhibitory Activities of Antioxidant Aminothiadiazoles Against the COVID-19 Omicron Virus: A Promising In Silico/In Vitro Repositioning Research Study
- PMID: 36690820
- PMCID: PMC9870775
- DOI: 10.1007/s12033-022-00551-8
Potent Dual Polymerase/Exonuclease Inhibitory Activities of Antioxidant Aminothiadiazoles Against the COVID-19 Omicron Virus: A Promising In Silico/In Vitro Repositioning Research Study
Abstract
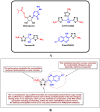
Recently, natural and synthetic nitrogenous heterocyclic antivirals topped the scene as first choices for the treatment of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections and their accompanying disease, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Meanwhile, the mysterious evolution of a new strain of SARS-CoV-2, the Omicron variant and its sublineages, caused a new defiance in the continual COVID-19 battle. Hitting the two principal coronaviral-2 multiplication enzymes RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease (ExoN) synchronously using the same ligand is a highly effective novel dual pathway to hinder SARS-CoV-2 reproduction and stop COVID-19 progression irrespective of the SARS-CoV-2 variant type since RdRps and ExoNs are widely conserved among all SARS-CoV-2 strains. Herein, the present computational/biological study screened our previous small libraries of nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds, searching for the most ideal drug candidates predictably able to efficiently act through this double approach. Theoretical filtration gave rise to three promising antioxidant nitrogenous heterocyclic compounds of the 1,3,4-thiadiazole type, which are CoViTris2022, Taroxaz-26, and ChloViD2022. Further experimental evaluation proved for the first time, utilizing the in vitro anti-RdRp/ExoN and anti-SARS-CoV-2 bioassays, that ChloViD2022, CoViTris2022, and Taroxaz-26 could effectively inhibit the replication of the new virulent strains of SARS-CoV-2 with extremely minute in vitro anti-RdRp and anti-SARS-CoV-2 EC50 values of 0.17 and 0.41 μM for ChloViD2022, 0.21 and 0.69 μM for CoViTris2022, and 0.23 and 0.73 μM for Taroxaz-26, respectively, transcending the anti-COVID-19 drug molnupiravir. The preliminary in silico outcomes greatly supported these biochemical results, proposing that the three molecules potently strike the key catalytic pockets of the SARS-CoV-2 (Omicron variant) RdRp's and ExoN's vital active sites. Moreover, the idealistic pharmacophoric hallmarks of CoViTris2022, Taroxaz-26, and ChloViD2022 molecules relatively make them typical dual-action inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication and proofreading, with their highly flexible structures open for various kinds of chemical derivatization. To cut it short, the present pivotal findings of this comprehensive work disclosed the promising repositioning potentials of the three 2-aminothiadiazoles, CoViTris2022, Taroxaz-26, and ChloViD2022, to successfully interfere with the crucial biological interactions of the coronaviral-2 polymerase/exoribonuclease with the four principal RNA nucleotides, and, as a result, cure COVID-19 infection, encouraging us to rapidly start the three drugs' broad preclinical/clinical anti-COVID-19 evaluations.
Keywords: 2-Amino-1,3,4-thiadiazole Derivative; Anti-COVID-19 Drug; Anti-Omicron Agent; ChloViD2022; Coronaviral-2 RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp); SARS-CoV-2 Proofreading 3′-to-5′ Exoribonuclease (ExoN).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors hereby declare that they totally have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this new research paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Strong Dual Antipolymerase/Antiexonuclease Actions of Some Aminothiadiazole Antioxidants: A Promising In-Silico/In-Vitro Repurposing Research Study against the COVID-19 Omicron Virus (B.1.1.529.3 Lineage).Adv Redox Res. 2023 Jan 26:100064. doi: 10.1016/j.arres.2023.100064. Online ahead of print. Adv Redox Res. 2023. PMID: 36776420 Free PMC article.
-
A Series of Adenosine Analogs as the First Efficacious Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Drugs against the B.1.1.529.4 Lineage: A Preclinical Repurposing Research Study.ChemistrySelect. 2022 Dec 13;7(46):e202201912. doi: 10.1002/slct.202201912. Epub 2022 Dec 8. ChemistrySelect. 2022. PMID: 36718467 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Investigational Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agent Ensitrelvir "S-217622": A Very Promising Potential Universal Broad-Spectrum Antiviral at the Therapeutic Frontline of Coronavirus Species.ACS Omega. 2023 Jan 30;8(6):5234-5246. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03881. eCollection 2023 Feb 14. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 36798145 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the interaction of nucleoside analogues with SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jun 30;181:605-611. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.112. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33766591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Candidates against COVID-19 Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase: A Comprehensive Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23(3):396-419. doi: 10.2174/1389201022666210421102513. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 33882805 Review.
Cited by
-
An efficient eco-friendly, simple, and green synthesis of some new spiro-N-(4-sulfamoyl-phenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-carboxamide derivatives as potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 proteases: drug-likeness, pharmacophore, molecular docking, and DFT exploration.Mol Divers. 2024 Feb;28(1):249-270. doi: 10.1007/s11030-023-10761-0. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 37946070 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Study of Flavonoids From Genus Erythrina As Ace2 inhibitor Candidates For Covid-19 Treatment.Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2024 May 14;17:61-70. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S454961. eCollection 2024. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2024. PMID: 38764460 Free PMC article.
-
Promising Experimental Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agent "SLL-0197800": The Prospective Universal Inhibitory Properties against the Coming Versions of the Coronavirus.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 18;8(39):35538-35554. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c08073. eCollection 2023 Oct 3. ACS Omega. 2023. Retraction in: ACS Omega. 2025 Mar 31;10(14):14554. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01901. PMID: 37810715 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Discovery of Hybrid Thiouracil-Coumarin Conjugates as Potential Novel Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents Targeting the Virus's Polymerase "RdRp" as a Confirmed Interacting Biomolecule.ACS Omega. 2023 Jul 14;8(30):27056-27066. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02079. eCollection 2023 Aug 1. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37546653 Free PMC article.
-
Strong Dual Antipolymerase/Antiexonuclease Actions of Some Aminothiadiazole Antioxidants: A Promising In-Silico/In-Vitro Repurposing Research Study against the COVID-19 Omicron Virus (B.1.1.529.3 Lineage).Adv Redox Res. 2023 Jan 26:100064. doi: 10.1016/j.arres.2023.100064. Online ahead of print. Adv Redox Res. 2023. PMID: 36776420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaur H, Sarma P, Bhattacharyya A, Sharma S, Chhimpa N, Prajapat M, Prakash A, Kumar S, Singh A, Singh R, Avti P, Thota P, Medhi B. Efficacy and safety of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitors “leflunomide” and “teriflunomide” in Covid-19: A narrative review. European Journal of Pharmacology. 2021;906:174233. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174233. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

