Phase 2 results of idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel, bb2121) in Japanese patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma
- PMID: 36690910
- PMCID: PMC10121508
- DOI: 10.1007/s12185-023-03538-6
Phase 2 results of idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel, bb2121) in Japanese patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma
Abstract
Background: In the phase 2 KarMMa trial, patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) achieved deep and durable responses with idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel), a B-cell maturation antigen-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy. Here we report a sub-analysis of the Japanese cohort of KarMMa.
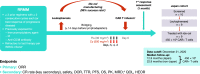
Methods: Adult patients with RRMM who had received ≥ 3 prior treatment regimens, including a proteasome inhibitor, an immunomodulatory agent, and an anti-CD38 antibody, and had disease refractory to last treatment received ide-cel at a target dose of 450 × 106 CAR positive T cells.
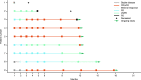
Results: Nine patients were treated with ide-cel. The overall response rate was 89% (median follow-up, 12.9 months). The best overall response was stringent complete response in 5 patients (56%), very good partial response in 3 (33%), and stable disease in 1. Median duration of response was not reached. All patients experienced grade ≤ 2 cytokine release syndrome and one patient experienced grade 2 neurotoxicity, but all resolved. Two patients died, one each from plasma cell myeloma and general health deterioration.
Conclusion: Ide-cel yielded deep, durable responses with a tolerable and predictable safety profile in Japanese patients with RRMM. These results are similar to those of the non-Japanese population in KarMMa.
Keywords: CAR T cell therapy; Idecabtagene-vicleucel; Japanese patients; Relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma; Triple-class exposed.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DM: nothing to declare. TI: grants or contracts from Alexion, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Pfizer, and Takeda; payment or honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, ONO, Sanofi, and Takeda. KA: research funding from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, and Takeda. RS: payment or honoraria from Janssen. JT: nothing to declare. SH: research funding from and participation on advisory board for Bristol Myers Squibb. RA: employee and stockholder of Bristol Myers Squibb; leadership or fiduciary role in other board, society, committee, or advocacy group for ASA NJ Princeton-Trenton Chapter (President). SK and MN: employee and stockholder of Bristol Myers Squibb K.K. YK: research grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, ONO, and Takeda; payment or honoraria for lectures from Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Novartis, Sanofi, and Takeda. KS: honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Novartis, ONO, Sanofi, and Takeda; consulted for Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Takeda; received research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma.N Engl J Med. 2021 Feb 25;384(8):705-716. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024850. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 33626253 Clinical Trial.
-
Early Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Expansion Is Associated with Prolonged Progression-Free Survival for Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Treated with Ide-Cel: A Retrospective Monocentric Study.Transplant Cell Ther. 2024 Jun;30(6):630.e1-630.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2024.03.003. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Transplant Cell Ther. 2024. PMID: 38458477
-
Idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel) CAR T-cell therapy for relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma.Future Oncol. 2022 Jan;18(3):277-289. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-1090. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Future Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34854741 Review.
-
Ide-cel or Standard Regimens in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma.N Engl J Med. 2023 Mar 16;388(11):1002-1014. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2213614. Epub 2023 Feb 10. N Engl J Med. 2023. PMID: 36762851 Clinical Trial.
-
Recent Advances in the Use of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Expressing T-Cell Therapies for Treatment of Multiple Myeloma.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023 Jan;23(1):22-27. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2022.09.001. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023. PMID: 36411210 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant on Safety and Outcomes of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell (CAR-T) Therapy in Patients with Multiple Myeloma (MM).J Clin Med. 2024 Oct 18;13(20):6207. doi: 10.3390/jcm13206207. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39458157 Free PMC article.
-
Elranatamab in Japanese patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: results from MagnetisMM-2 and MagnetisMM-3.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 4;54(9):991-1000. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyae068. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38794892 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of chimeric antigen receptor T cells targeting BCMA and GPRC5D in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 23;15:1466443. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466443. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39763668 Free PMC article.
-
Current landscape of innovative drug development and regulatory support in China.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jul 22;10(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02267-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40691459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measurable Residual Disease Testing in Multiple Myeloma Following T-Cell Redirecting Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;16(19):3288. doi: 10.3390/cancers16193288. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409909 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

