Assessment of motor function and nutritional status in children with spinal muscular atrophy treated with nusinersen after loading period in Western China: a retrospective study
- PMID: 36690929
- PMCID: PMC9869561
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-023-03063-3
Assessment of motor function and nutritional status in children with spinal muscular atrophy treated with nusinersen after loading period in Western China: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a progressive degenerative neuromuscular disease. Nusinersen, with its quick onset of action, can benefit patients early in the treatment course. However, there are currently no clinical studies regarding the improvement in motor function and nutritional status of patients after loading period treatment with nusinersen. Here, we aimed to determine the efficacy of nusinersen in improving motor function and nutritional status in children with SMA treated with nusinersen after loading period in Western China.
Methods: In this retrospective study, data for all pediatric patients (aged < 18 years), with genetically confirmed diagnosis of SMA who were treated with nusinersen, were collected before initiation of treatment and after 2 months of treatment. We assessed motor function using standardized scales and nutritional status of patients with SMA as well as side effects of nusinersen.
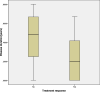
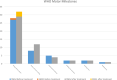
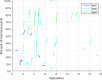
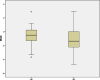
Results: Forty-six pediatric patients aged < 18 years were enrolled in this study. After 2 months of treatment, the motor function of patients with SMA type 1, 2, and 3 improved. The difference in Revised Upper Limb Module scores from M0 to M2 was significant in patients with SMA type 2 and 3 (P = 0.004, P = 0.042, respectively). The difference in Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale Expanded scores from M0 to M2 in patients with SMA type 2 was also significant (P = 0.000). No significant differences were found for Children's Hospital of Philadelphia Infant Test of Neuromuscular Disorder (CHOP-INTEND), Hammersmith Infant Neurologic Examination-Part 2 (HINE-2), and 6-Minute Walking Test (6MWT) scores between M0 and M2, but the scores of CHOP-INTEND, HINE-2, and 6MWT were all increased after loading period treatment. The overall improvement in nutritional status was not statistically significant. No serious adverse effects were observed.
Conclusions: Our study provides evidence for the efficacy and safety of nusinersen and the nutritional status of pediatric patients with SMA after the loading period treatment. Motor function of all patients improved after 2 months of loading period nusinersen treatment. Patients with a shorter disease duration showed better response to treatment. Careful surveillance of nutritional status is needed in patients with SMA.
Keywords: Children; Motor function measure; Nusinersen; Nutritional status; Spinal muscular atrophy.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wei X, Tan H, Yang P, Zhang R, Tan B, Zhang Y, et al. Notable carrier risks for individuals having two copies of SMN1 in spinal muscular atrophy families with 2-copy alleles: estimation based on Chinese meta-analysis data. J Genet Couns. 2017;26(1):72–78. doi: 10.1007/s10897-016-9980-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weaver JJ, Natarajan N, Shaw DWW, Apkon SD, Koo KSH, Shivaram GM, et al. Transforaminal intrathecal delivery of nusinersen using cone-beam computed tomography for children with spinal muscular atrophy and extensive surgical instrumentation: early results of technical success and safety. Pediatr Radiol. 2018;48(3):392–397. doi: 10.1007/s00247-017-4031-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- WHO Motor Development Study Windows of achievement for six gross motor development milestones. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 2006;450:86–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2021YFC1005305/the National Key R&D Program of China
- No.2020YFQ0021/Sichuan Provincial Key Laboratory of Shock and Vibration of Engineering Materials and Structures, Southwest University of Science and Technology
- No. 82071686/Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

